Basics of Phase Change Memory
Phase Change Memory (PCM) animation
Catalog
Ⅰ Introduction
Phase change random access memory, P-RAM, is a type of non-volatile memory or computer storage that is faster than the Flash memory system that is far more widely used. A variety of terms, like P-RAM or PRAM, PC-RAM, phase change RAM, and probably more, may be used to refer to phase change memory. Phase shift memory is based on a technique originally developed by Hewlett Packard, known as the memresitor.
A number of other suppliers have also taken up phase shift memory and are expected to see growing use. Phase shift memory is seen as a big development and one that is expected to become one of the future standard semiconductor memory formats.
The phase change memory, PCM, or random access memory of phase change, P-RAM, uses the special property of a material called chalcogenide glass.

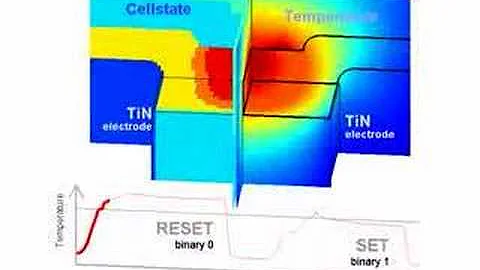
Phase Change Memory
The P-RAM uses the fact that the chalcogenide glass shifts through the passing of current that generates heat when it travels through a cell into two states, polycrystalline and amorphous. As the material transitions between the two states or stages, this gives rise to the term phase transition.
The substance displays a high degree of resistance and even poor reflectivity in the amorphous state.

Architecture of PCM
The substance has a normal crystalline form in the polycrystalline state, and this expresses itself in a change in properties. It has a low resistance in this state so electrons can pass freely through the crystalline structure, and it also shows a high reflectivity.
It is the resistance level that is of concern for phase shift storage / phase change RAM. The circuitry around the cell then senses the resistance shift when the two states have a different resistance and then detects if there is a "1" or "0" stored in that position.
As a result of injection current for a timed duration, the phase transition between the two states of the chalcogenide is brought on by localized heating. The amplitude of the injected current and the time of the process modulate the final step of the substance.
The heating is given by a resistive element - it reaches from the bottom electrode to the chalcogenide base. Heat that is then transmitted to the chalcogenide layer is given by the current passing through the resistive heater portion. In addition, two additional states have recently developed the technology, essentially doubling the storage of a given-sized unit.
The promise of PCM has been seen in a wide variety of works over the past 10 years as a pure memory technology, and the only remaining problems are arguably linked to cost, product-level development and high-level incorporation into a computer device. The successful introduction of Intel Optane in 2018, a PCM-based non-volatile memory that can be used to boost the current memory storage infrastructure, shows the possibility of using PCM in a traditional operating system as a digital memory. Because of this, a thorough understanding of PCM's fundamental physical processes and state dynamics is necessary for working out how to further refine the technology.
Ⅱ Advantages & disadvantages
1.Advantages of phase change memory
Non-volatile: Phase change RAM is a non-volatile type of memory, i.e. the retention of its data does not require power. This helps it to specifically compete with flash memory.
Bit alterable: P-RAM / PCM is what is considered bit-alterable, equivalent to RAM or EEPROM. This means that without the need for a deleting process, data can be written directly to it. This gives it a major advantage over flash that needs a period of deletion before it can be written to new files.
Fast read performance: Rapid random access times are given by Phase change RAM, P-RAM / PCM. This has the bonus that it allows code to be run directly from the memory, without the need to copy the data to RAM. The P-RAM read latency is equivalent to one bit per NOR flash cell, while the read bandwidth is close to that of DRAM.
Fast read performance: Phase change RAM, P-RAM / PCM features fast random access times. This has the bonus that it allows code to be run directly from the memory, without the need to copy the data to RAM. The P-RAM read latency is equivalent to one bit per NOR flash cell, while the read bandwidth is close to that of DRAM.
Scalability: Another aspect where it may have benefits is the scalability of P-RAM for the future, but this is yet to be understood. The logic is that both NOR and NAND flash variants depend on hard-to-shrink floating gate memory structures. If the memory cell size is decreased, it is observed that the amount of electrons deposited on the floating gate is reduced and this makes it more difficult to identify these smaller charges accurately. P-RAM does not store a charge, but depends on a shift in resistance instead. As a consequence, it is not vulnerable to the same issues of scaling.
Write/erase performance: phase change memory's erase performance is very strong with higher speeds and lower latency than NAND flash. Because no deletion phase is needed, this offers a major overall improvement over flash.
2.Disadvantages of phase change memory
Economic viability: Despite the numerous promises regarding the benefits of P-RAM, few enterprises have been able to produce chips that have been commercialized successfully.
Multiple bit storage per Flash cell: Flash's ability to store and detect multiple bits per cell also gives Flash an advantage over P-RAM in memory space. Although P-RAM / PCM has benefits for the future in potential scalability.
Both the positives and drawbacks need to be weighed when looking at using phase change memory.
A number of manufacturers have implemented phase change memory, but it is still not commonly used as many developers might be skeptical of a modern invention like this. Nevertheless, PCM has many distinct benefits to deliver on a variety of instances in phase change memory.
Ⅲ Different Companies’ Phase Change Memory
As described above, phase change memory is a product that is seeing substantial investment from major suppliers. Multiple manufacturers have been openly discussing their PCM activities and technologies with differing degrees of success at this stage.
IBM
PCM storage innovations working on its OpenPower server architecture have been shown by IBM.
A three bit per cell PCM chip is among IBM's research developments, which could provide more stability and storage than previous research which demonstrated 1 bit per cell options.
Intel
Since at least 2006, Intel has been working on PCM, when it unveiled the platform at its developer conference.
Any components of PCM may be part of the 3D XPoint technologies of the business, but a dedicated PCM solution is not currently directly advertised by Intel.
Micron
Thanks in part to its 2010 purchase of PCM leader Numonyx, Micron has been among the leading suppliers developing PCM technology.
Micron revealed that it was leaving the PCM market in 2014 following several fits and starts.
Samsung
For over a decade, Samsung has been focusing on diverse versions of PCM technology.
The key use case that the business is currently working on is for embedded use inside mobile phones, but there is still the possibility for possible commercial storage systems.
STMicroelectronics
One of the core patents that allows PCM storage is held by STMicrolectonics.
For automotive use cases, the company has been developing embedded PCM (ePCM) technology.
Digital Western
The HGST (Hitachi Global Storage Technologies) business unit of Western Digital has been developing a technology called DC Express to help fully enable PCM storage for a future motherboard generation.
1.What is a phase change memory device?
Phase-change memory (PCM) is a key enabling technology for non-volatile electrical data storage at the nanometer scale. A PCM device consists of a small active volume of phase-change material sandwiched between two electrodes. The stored data can be retrieved by measuring the electrical resistance of the PCM device.
2.What are the challenges in the phase change memory?
Probably the biggest challenge for phase-change memory is its long-term resistance and threshold voltage drift. The resistance of the amorphous state slowly increases according to a power law (~t0.1).
3.What are PCMs used for?
PCMs are used in many different commercial applications where energy storage and/or stable temperatures are required, including, among others, heating pads, cooling for telephone switching boxes, and clothing. By far the biggest potential market is for building heating and cooling.
 How to Use an External Hard Drive?UTMEL24 June 20218854
How to Use an External Hard Drive?UTMEL24 June 20218854The external hard drive is a compact and portable hard drive storage which can be plugged in or unplugged at any time. It mainly uses USB or IEEE1394 interfaces. It can transmit data with the system at a higher speed. The IEEE 1394 interface transfer rate is 50-100 MB/s.
Read More Introduction to RAID (Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks)UTMEL01 July 20218343
Introduction to RAID (Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks)UTMEL01 July 20218343RAID (Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks) means "a redundant array composed of independent disks". The RAID is the combination of many independent disks that combined into a large-capacity disk group. It uses the bonus effect of individual disks to provide data to enhance the performance of the entire disk system.
Read More What is NAND Flash?UTMEL04 November 202111035
What is NAND Flash?UTMEL04 November 202111035NAND Flash is a better storage device than hard disk drives and is particularly evident in low-volume applications up to 4GB. As the quest continues for lower power consumption, lighter weight, and better performance, NAND is proving to be very attractive. Its development goal is to reduce the cost per bit of storage and increase storage capacity.
Read More Memory Chip: The Key to Smart ConnectivityUTMEL03 November 20212445
Memory Chip: The Key to Smart ConnectivityUTMEL03 November 20212445In today's post, we talk about memory chips, especially their emerging applications in the AIoT smart interconnect space.
Read More Emerging Storage Technologies: MRAM, RRAM, and PCRAMUTMEL08 January 20269500
Emerging Storage Technologies: MRAM, RRAM, and PCRAMUTMEL08 January 20269500The semiconductor industry is turning to emerging memories that offer higher storage performance, lower cost, and the ability to move toward process miniaturization. Three of these memories stand out -- MRAM, RRAM, and PCRAM.
Read More
Subscribe to Utmel !




