Solenoid Switch: Working Principle, Types and Applications
How solenoid switch works?
Catalog
| I. Working Principle |
| II. Types |
| III. Applications |
Using a small electrical control signal, solenoid switches are used in high voltage circuits for switching purposes. This transition primarily uses decision-making to operate on economical microchips & tiny electronic parts as well as comprehensive logic circuits. It also allows the switching apparatus of high power to be limited to a remote area. In cars, these switches are usually used to start the engine systems. An description of what a solenoid switch is and its operation is discussed in this article.
I. Working Principle
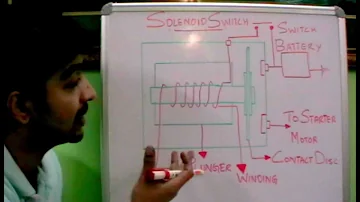
Wire wound magnetic coils, with an open heart, are solenoid switches to receive a cylindrical sliding plunger. A magnetic field can occur inside the hollow opening once the coil is triggered, which drags the cylindrical plunger into it depending on the direction of the switch as well as the poles of the plunger. Here, the plunger link can be made mechanically to conduct the high-power switching to a series of switch contacts.
There are four connector terminals on a solenoid switch, where the coil uses two and can most often be separated from all the remaining terminals. That keeps the coil fully autonomous. Generally, relative to the terminals of the coil, the terminals of the switched current are considerably heavier.

II. Types
Due to the flow of current through them, most of these switches have just one switched pole. Some switches work like starter solenoids used in cars for just a moment. When a car's engine is activated, both the engine starter and the switch are fully disconnected from the electrical system. The moving plunger for sliding the starter pinion with the starter shaft is used in some automotive systems. It connects the flywheel to the starter motor and also provides power.
There are different forms of solenoids on the market that are available. In terms of their fabrics, design and feature, they vary. But the same electrical principles rely on all sorts of solenoids:
AC Laminated Solenoid
DC C-Frame Solenoid
DC D-Frame Solenoid
Linear Solenoid
Rotary Solenoid
In a tube or conduit, a solenoid valve controls the flow of fluid. In order to control the media, different mechanisms are used, which ensures that a wide variety of these valves cater to the variations.
These valves come with distinct operating mechanisms in addition to the designs. Here, we take a look at the 5 types and working concepts of solenoid valves:
- Direct Acting Solenoid Valve
These types of valves employ the easiest operation to run. A direct-acting solenoid valve consists of a plunger that, without relying on an external force, directly closes a small orifice.
These solenoid valve styles are fast-acting. They can also work from the lowest to the highest permissible levels under various pressures.
An NO (normally open) or NC (normally closed) valve may be a direct-acting solenoid valve. If the NO valve is used, the orifice closes when an electric current is applied.
The orifice stays closed and opens in an NC, direct acting valve when the solenoid coil windings are energized.
The three way 2 place solenoid valve is a version of the direct acting valve. It functions identically with the 2/2 valve, with only variations in the way fluid is exhausted. With a seal at the top or bottom of the plunger, it may do so.
There are benefits and drawbacks to the use of direct acting solenoid valves. Such valves are fast-acting and precise. Another benefit is that these types of valves, from low to high, will operate with different line pressures.
The downsides of solenoid valves that function directly are mainly in their strength and scale. Since the valves rely on the solenoid coil's closing power, they normally need a lot of current to work.
- Pilot-Operated Solenoid Valve
A pilot solenoid valve, also called an indirect-operated valve, uses the pressure difference to close or open the orifice between the valve ports. The function of these types of valves is much more complicated and with a few more parts than that of direct acting valves.
Here is how it operates with the pilot solenoid valve.
The inlet and outlet ports of these kinds of solenoid valves are separated by a diaphragm. A small hole is in the diaphragm that allows the medium to pass into the upper chamber. This chamber is connected to the low-pressure port by a narrow duct.
This results in the raising of the diaphragm and the medium are now free to flow from the inlet to the outlet port.
In a pilot-operated solenoid valve, the pressure chamber helps to intensify the closing and opening forces. This allows a high-flow line to be powered by tiny solenoids.
Due to this pressure amplification, this type of solenoid valve usually does not require large quantities of current to operate.
Pilot solenoid valves have many drawbacks, despite their powerful operation. They are a one-way solenoid valve, able to control a medium that flows in one direction only.
- Two Way Solenoid Valves
Two ports are used by these valve types to close or open the fluid flow. If the orifice allows media to flow while the coil is de-energized and normally closed, if energizing the coil allows fluid to flow through either port, a 2-way solenoid valve is known as normally open. It is more common than the NO type to use the NC or usually closed solenoid valve.
Two-way solenoid control valve systems where it is only important to release and limit media. These include machines and similar devices for air compression.
- Three Way Solenoid Valve
With three ports and two separate orifices, a 3-way solenoid valve normally comes fitted. According to the condition of the solenoid coil, the two orifices open alternatively.
These valve types usually have two inlet ports and a single outlet. A three-way solenoid valve often combines two separate fluids when used in this configuration.
Two outlets and a single inlet port are used by certain three-way solenoid valves. In one of the outlet ports, this kind of design allows the valve to regulate the flow of a medium by steering it into the other. In common home appliances, such as the household dishwasher, 3-way solenoid valves can be found.
- Four-Way Solenoid Valve
Four ports are used by this type of valve; two pressure inlets and two exhaust outlets. For controlling double-acting solenoid valve actuators, 4-way valves are widely used.
The inlet ports supply the actuator or cylinder with incoming pressures, and exhaustive pressure openings are the outlet pipes.
III. Applications
The applications for solenoid switch specifically include the following.
Using small electrical control signals for switch activation, the solenoid switch is used to control high-power circuits.
It also enables a system for high-power switching to be confined to a remote location.
These switches are normally used in automotive engine starting systems.
- Solenoid Switch in Automobile:
In automobiles, the position of the solenoid switch includes the following.
Solenoids carry a current which generates a magnetic field when energized. This magnetic field provides a power source with high force and current for triggering devices used in electrical and vehicle applications, such as automotive and industrial applications.
A reliable switch that connects the battery of the vehicle to the starter motor is activated by the solenoid switch.
Once the ignition key is in the initial position, the pinion of the starter is connected by this switch.
How to Wire a Solenoid Switch?
These switches are primarily used to control the circuit with a wide current using a low-current switch. These devices have a high current switch that is operated by a magnetic actuator known as a solenoid. Once the solenoid supplies small current, then the center of this will shift to the force transfer that has high current to the closed position. It involves four terminals, based on the solenoid size. Therefore, for low current circuits, two terminals are used, while for the high current circuit of the solenoid, the remaining terminals are used. There are distinct steps, such as the following, to connect a solenoid switch: Attach the high-current switch terminals to the solenoid switch, and then follow the documentation given for the location of the two terminals using the switch. Slash two pieces of black wire and tie the battery terminal to one end of the original black wire. Similarly, mount the second end of the wire to one of the switch's high-current terminals. Link the other black wire to the switch's other high-current terminal. After that, connect the DC motors-ve terminal to the next end of the comparable cable. Slash one section of red wire and connect one end to the engine's +ve terminal and attach the other end to the battery's +ve terminal. To be able to form a high current circuit. Slash two black wire components & connect one end of the primary wire over the switch to the original low current terminal. Connect the remaining terminal to one of the 6V transfer terminals and the remaining terminal can be linked to the 6V battery's-Ve terminal. Arrange one red color cable between the battery's +ve terminal and fix the remaining end over the switch to the next low-current terminal. So a circuit of low current can be created. Finally, the 6V switch is turned on and then the DC motor starts running.
How does a solenoid switch work?
When the ignition switch is turned on, a small electric current is sent through the starter solenoid. This causes the starter solenoid to close a pair of heavy contacts, thus relaying a large electric current through the starter motor, which in turn sets the engine in motion.
Is a solenoid a switch?
A solenoid switch is an electrical switch that is often used where a high current circuit, such as a starter motor circuit, is brought into operation by a low current switch. When the key switch is turned to Start and the gearshift is in neutral, the circuit between the battery and the solenoid switch is complete.
 Long Life Small Volume Detector Switch for Intelligent ApplicationsUTMEL16 March 20222662
Long Life Small Volume Detector Switch for Intelligent ApplicationsUTMEL16 March 20222662Hello everyone, I am Rose. Welcome to the new post today. This article will introduce what is a detection switch, how to choose a detection switch and where to use a detection switch.
Read More Analog Switch: Types and ApplicationUTMEL25 March 202111441
Analog Switch: Types and ApplicationUTMEL25 March 202111441The analog switch is mainly to complete the signal switching function in the signal chain. The switching mode of the MOS tube is adopted to realize the switching off or on of the signal link.
Read More Toggle Switches: Features, Types and ApplicationsUTMEL23 January 20218594
Toggle Switches: Features, Types and ApplicationsUTMEL23 January 20218594Toggle switch adopts integrated circuit technology and SMT appearance device technology to manufacture a new generation of photoelectric switch devices. It has intelligent functions such as delay, expansion, external synchronization, anti-interference, high reliability, stable working area, and self-diagnosis. This novel photoelectric switch is an active photoelectric detection system electronic switch that uses pulse modulation. The cold light source used is infrared light, red light, green light and blue light, etc., which can be quickly and without contact and damage Control the state and action of various solid, liquid, transparent, black, soft, smoke and other substances.
Read More DIP Switch: Introduction and ClassificationUTMEL20 January 202111713
DIP Switch: Introduction and ClassificationUTMEL20 January 202111713DIP switch is an address switch used for operation control, using the principle of 0/1 binary coding. It is a miniature switch that can be toggled by hand. Dip switches are widely used in data processing, communication, remote control and anti-theft automatic alarm systems and other products that require manual programming.
Read More Solenoid Switch: Working Principle, Types and ApplicationsUTMEL03 February 202123507
Solenoid Switch: Working Principle, Types and ApplicationsUTMEL03 February 202123507A solenoid switch is an electrical switch that is often used where a high current circuit, namely a starter motor circuit, is brought into operation with the aid of a low current switch. This switch switches a durable switch on to connect the vehicle's battery to the starter of the motor. A solenoid switch attaches the drive pinion to the starter until the ignition key is triggered. High performance, reliability, and longevity are the key characteristics of solenoid switches.
Read More
Subscribe to Utmel !
![FLUKE-1623-2]() FLUKE-1623-2
FLUKE-1623-2Fluke Electronics
![1081-4-2]() 1081-4-2
1081-4-2Pomona Electronics
![5302-36-2]() 5302-36-2
5302-36-2Pomona Electronics
![Z10-40-L-U]() Z10-40-L-U
Z10-40-L-UTDK-Lambda Americas Inc.
![Z20-30-IS420-U]() Z20-30-IS420-U
Z20-30-IS420-UTDK-Lambda Americas Inc.
![Z10-60-IS510-U]() Z10-60-IS510-U
Z10-60-IS510-UTDK-Lambda Americas Inc.
![ZUP6-33/LU]() ZUP6-33/LU
ZUP6-33/LUTDK-Lambda Americas Inc.
![1440-18-2]() 1440-18-2
1440-18-2Pomona Electronics
![FLUKE-705]() FLUKE-705
FLUKE-705Fluke Electronics
![2864-24-2]() 2864-24-2
2864-24-2Pomona Electronics












