TMC2208 vs. TMC2209: What Differences is between them?
900μm mm 5mm mm Motor Drivers 28 24V V 5V V 5mm mm
TMC22XX are the ultra-silent motor driver ICs for two-phase stepper motors. This post will unlock the difference between TMC2208 and TMC2209, including their datasheet, pinout, feature, application and more angles from them.
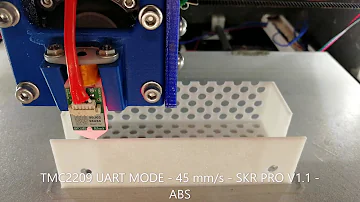
TMC2209 V1 2 UART MODE vs A4988 vs TMC2208 V3 SPI noise test
TMC2208 vs. TMC2209 Pinout

TMC2208 vs. TMC2209 Pinout
TMC2208 vs. TMC2209 Overview
The TMC22XX are ultra-silent motor driver ICs for two-phase stepper motors. Their pinning is compatible with a number of legacy drivers. TRINAMICs sophisticated StealthChop2 chopper ensures noiseless operation, maximum efficiency and best motor torque. Its fast current regulation and optional combination with SpreadCycle allow for highly dynamic motion. Integrated power MOSFETs handle motor current up to 1.4 ARMS. Protection and diagnostic features support robust and reliable operation. A simple to use UART interface opens up more tuning and control options. Application-specific tuning can be stored in OTP memory. Industries’ most advanced STEP/DIR stepper motor driver family upgrades design to noiseless and most precise operation for cost-effective and highly competitive solutions.
TMC2209 pinning is compatible with a number of legacy drivers as well as with the TMC2208. TRINAMICs sophisticated StealthChop2 chopper ensures noiseless operation, maximum efficiency and best motor torque. Its fast current regulation and optional combination with SpreadCycle allow highly dynamic motion while adding. Stallard for sensorless homing.
TMC2208 vs. TMC2209 Feature & Benifit
| TMC2208 | TMC2209 |
| 2-phase stepper motors up to 2A coil current (peak) | 2-phase stepper motors up to 2.8A coil current (peak), 2A RMS |
| STEP/DIR Interface with 2, 4, 8, 16 or 32 micro steps pin setting | STEP/DIR Interface with 8, 16, 32 or 64 micro steps pin setting |
| Smooth Running 256 micro steps by MicroPlyerTM interpolation | Smooth Running 256 micro steps by MicroPlyerM interpolation |
| StealthChop2TM silent motor operation | StealthChop2TM silent motor operation |
| SpreadCycleTM highly dynamic motor control chopper | SpreadCycleTM highly dynamic motor control chopper |
| Low RDSon LS 280mΩ & HS 290mΩ (typ. at 25℃ | StallGuard4TH load and stall detection for StealthChop |
| Voltage Range 4... 36V DC | CoolStepM current control for energy savings up to 75% |
| Automatic Standby current reduction (option) | Low RDSon, Low Heat-Up LS 170mΩ & HS 170mΩ(typ. at 25℃ |
| Internal Sense Resistor option (no sense resistors required) | Voltage Range 4.7.. 29V DC |
| Passive Braking and Freewheeling | Low Power Standby to fit standby energy regulations |
| Single Wire UART & OTP for advanced configuration options | Internal Sense Resistor option (no sense resistors required) |
| Integrated Pulse Generator for standalone motion | Passive Braking, Freewheeling, and automatic power down |
| Full Protection & Diagnostics | Single Wire UART & OTP for advanced configuration options |
| Choice of QFN and wettable QFN packages for best fit | Integrated Pulse Generator for standalone motion |
| Full Protection & Diagnostics | |
| Compact QFN package with a large heat slug |
TMC2208 vs. TMC2209 Block Diagram
The following figures show the block diagram of TMC2208 and TMC2209

TMC2208 Block Diagram

TMC2209 Block Diagram
The TMC22xx family scores with power density, integrated power MOSFETs, smooth and quiet operation, and a congenial simplicity. The TMC22xx covers a wide spectrum of applications from battery systems to embedded applications with up to 2 A motor current per coil. TRINAMICs unique chopper modes SpreadCycle and StealthChop2 optimize drive performance. StealthChop reduces motor noise to the point of silence at low velocities. Standby current reduction keeps costs for power dissipation and cooling down. Extensive support enables rapid design cycles and fast time-to-market with competitive products.
TMC2208 vs. TMC2209 Application Circuit

TMC2208 Application Circuit

TMC2209 Application Circuit
The TMC22xx family of stepper drivers is intended as a drop-in upgrade for existing low-cost stepper driver applications. Its silent drive technology StealthChop enables non-bugging motion control for home and office applications. A highly efficient power stage enables high current from a tiny package.
The TMC2208 requires just a few control pins on its tiny package. They allow the selection of the most important setting: the desired micro step resolution. A choice of 2, 4, 8, 16 or 32 micro steps adapts the driver to the capabilities of the motion controller. Some package options also allow chopper mode selection by pin. The TMC2209 requires just a few control pins on its tiny package. It allows the selection of the most important setting: the desired micro step resolution. A choice of 8,16, 32 or 64 micro-steps, or from full step up to 1/256 step adapts the driver to the capabilities of the motion controller.
TMC2208 vs. TMC2209 Datasheet PDF
TMC2208 vs. TMC2209 Conclusion
Both the TMC2208 and TMC2209 support 1/256 stepping, both interpolated and native. They are both using StealthChop V2 for whisper-quiet printing. The TMC2208 was chosen over the TMC2209 for a variety of reasons related to the machines for which the board is designed and the design cycle of our board. Because they both use the same basic technologies to regulate the motors and have the same noise levels, there are no differences in print quality between 2208 and 2209.
Parts with Similar Specs
What does the TMC2208 and TMC 2209 support?
1/256 stepping.
What does the TMC2208 and TMC 2209 use for whisper-quiet printing?
StealthChop V2.
What do the TMC2208 and TMC 2209 use?
The same basic technologies regulate the motors and have the same noise levels.
What is the name of the ultra-silent motor driver ICs for two-phase stepper motors?
TMC22XX.
How many ARMs do MOSFETs handle?
1.4 ARMS.
What type of chopper is TRINAMIC?
StealthChop2 chopper.
What is used for sensorless homing?
Stallard.
How many control pins does the TMC2208 require on its tiny package?
A few control pins.
What does the TMC2209 allow the selection of the most important setting?
The desired micro step resolution.
 10M16DAU324I6G FPGA Device: Features, Specifications, Advantages
10M16DAU324I6G FPGA Device: Features, Specifications, Advantages14 August 2024758
 Texas Instruments MSP430F449IPZ Microcontroller Datasheet: Features, Applications, and Reference Designs
Texas Instruments MSP430F449IPZ Microcontroller Datasheet: Features, Applications, and Reference Designs29 February 2024117
 A Comprehensive Guide to Intel RealSense 82635DSITR50P Linear Video Processing Chip
A Comprehensive Guide to Intel RealSense 82635DSITR50P Linear Video Processing Chip11 March 2024397
 AT89S52-24PU Microcontroller: Diagram, Pinout, and Datasheet
AT89S52-24PU Microcontroller: Diagram, Pinout, and Datasheet04 March 20226992
 ADM3222ANZ Transceivers: Pinout, Specification, Datasheet
ADM3222ANZ Transceivers: Pinout, Specification, Datasheet27 May 2021457
 ZiLOG ZLP12840 OTP MCU: Product Overview
ZiLOG ZLP12840 OTP MCU: Product Overview29 February 2024163
 AT24CM01 Serial EEPROM: Pinout, Equivalent and Datasheet
AT24CM01 Serial EEPROM: Pinout, Equivalent and Datasheet24 December 20211529
 STM32F429ZIT6 for Industrial Automation: Complete Guide 2025
STM32F429ZIT6 for Industrial Automation: Complete Guide 202524 July 2025161
 Multivibrator: Circuits, Types and Application
Multivibrator: Circuits, Types and Application08 September 202023897
 What is a Capacitive Sensor?
What is a Capacitive Sensor?31 October 20259184
 Hall Effect: Definition, Principle, Measurement Methods
Hall Effect: Definition, Principle, Measurement Methods08 November 20228513
 How to Identify the Perfect Proximity Sensor for Your Application
How to Identify the Perfect Proximity Sensor for Your Application19 July 2025732
 Network Interface Card: Types, Functions and Buying Guide
Network Interface Card: Types, Functions and Buying Guide17 August 20218369
 What is Chiplet?
What is Chiplet?17 November 20213585
 How Big is the DV/DT and DI/DT of the Power Device?
How Big is the DV/DT and DI/DT of the Power Device?24 April 20228287
 Characteristics and Working Principle of IGBT
Characteristics and Working Principle of IGBT31 October 202518879
Trinamic Motion Control GmbH
In Stock: 5940
United States
China
Canada
Japan
Russia
Germany
United Kingdom
Singapore
Italy
Hong Kong(China)
Taiwan(China)
France
Korea
Mexico
Netherlands
Malaysia
Austria
Spain
Switzerland
Poland
Thailand
Vietnam
India
United Arab Emirates
Afghanistan
Åland Islands
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antigua & Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba
Bosnia & Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
Christmas Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo
Congo (DRC)
Cook Islands
Costa Rica
Côte d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curaçao
Cyprus
Czechia
Denmark
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia
Georgia
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Honduras
Hungary
Iceland
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Jamaica
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macao(China)
Madagascar
Malawi
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Myanmar
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Korea
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Palestinian Authority
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Réunion
Romania
Rwanda
Samoa
San Marino
São Tomé & Príncipe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
South Sudan
Sri Lanka
St Helena, Ascension, Tristan da Cunha
St. Barthélemy
St. Kitts & Nevis
St. Lucia
St. Martin
St. Pierre & Miquelon
St. Vincent & Grenadines
Sudan
Suriname
Svalbard & Jan Mayen
Sweden
Syria
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad & Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks & Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
U.S. Outlying Islands
U.S. Virgin Islands
Uganda
Ukraine
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Vatican City
Venezuela
Wallis & Futuna
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe















