74HC245 Transceiver IC: Price, Uses and Datasheet
DUAL Transceiver, Non-Inverting 2V~6V 3-State Buffers 74HC Series 74HC245 20 Pins 8 Bit per Element 20-SOIC (0.295, 7.50mm Width)









DUAL Transceiver, Non-Inverting 2V~6V 3-State Buffers 74HC Series 74HC245 20 Pins 8 Bit per Element 20-SOIC (0.295, 7.50mm Width)
Hello everyone, I am Rose. Today we will detail the introduction to 74HC245. The 74HC245 is a 3−state non-inverting transceiver that is used for asynchronous transfer of data communication between two devices. This article mainly introduce price, uses, datasheet and other detailed information about Nexperia 74HC245.
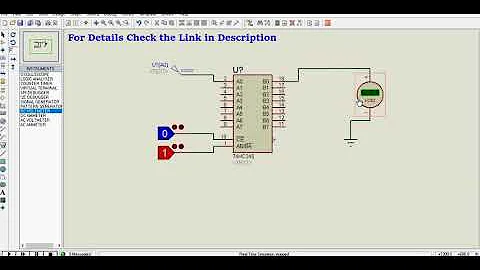
74HC245 Octal 3−State Non-inverting Bus Transceiver Proteus Simulation
74HC245 Description
The 74HC245 is a 3−state non-inverting transceiver that is used for asynchronous transfer of data communication between two devices. Furthermore, it supports data transfer at different voltage levels.
The device has an active−low Output Enable pin, which is used to place the I/O ports into high−impedance states. The Direction control determines whether data flows from A to B or from B to A.
The internal structure of a chip is composed of two amplifiers. Hence, it can perform two-way communication. This bidirectional communication is achieved by a signal applied at the direction control pin. It has very low input current and consumes less power.
These features make it suitable for a large number of applications. Low power consumption, wide voltage range, low input current are the major features associated with 74HC245. 74HC 245 is mostly used in personal computers, servers, wearable health devices, fitness devices, network switches, electronic points of sale etc.
74HC245 Pinout


74HC245 CAD Model
Symbol

Footprint

3D Model

74HC245 Features
●Lead free
●Supply Voltage Range : 2V to 6V
●Output Voltage is equal to Vcc
●Minimum Input Voltage: 0.8V
●Maximum Input Voltage: 4.2V
●Minimum Output Voltage: 1.9V
●Maximum Output Voltage: 5.4V
●Output Current: 35mA
●Off-State Output Current: 10uA
●Low input current :1A
●Propagation delay:13 ns.
●Non-Inverting, hence easy to interface
●Available in 20-pin SO20, SSOP20, TSSOP20 and DHVQFN20 packages
Specifications
- TypeParameter
- Factory Lead Time4 Weeks
- Mounting Type
The "Mounting Type" in electronic components refers to the method used to attach or connect a component to a circuit board or other substrate, such as through-hole, surface-mount, or panel mount.
Surface Mount - Package / Case
refers to the protective housing that encases an electronic component, providing mechanical support, electrical connections, and thermal management.
20-SOIC (0.295, 7.50mm Width) - Surface Mount
having leads that are designed to be soldered on the side of a circuit board that the body of the component is mounted on.
YES - Number of Pins20
- Number of Elements1
- Operating Temperature
The operating temperature is the range of ambient temperature within which a power supply, or any other electrical equipment, operate in. This ranges from a minimum operating temperature, to a peak or maximum operating temperature, outside which, the power supply may fail.
-40°C~125°C TA - Packaging
Semiconductor package is a carrier / shell used to contain and cover one or more semiconductor components or integrated circuits. The material of the shell can be metal, plastic, glass or ceramic.
Tape & Reel (TR) - Series
In electronic components, the "Series" refers to a group of products that share similar characteristics, designs, or functionalities, often produced by the same manufacturer. These components within a series typically have common specifications but may vary in terms of voltage, power, or packaging to meet different application needs. The series name helps identify and differentiate between various product lines within a manufacturer's catalog.
74HC - Published2011
- JESD-609 Code
The "JESD-609 Code" in electronic components refers to a standardized marking code that indicates the lead-free solder composition and finish of electronic components for compliance with environmental regulations.
e4 - Part Status
Parts can have many statuses as they progress through the configuration, analysis, review, and approval stages.
Active - Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL)
Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) is a standardized rating that indicates the susceptibility of electronic components, particularly semiconductors, to moisture-induced damage during storage and the soldering process, defining the allowable exposure time to ambient conditions before they require special handling or baking to prevent failures
1 (Unlimited) - Number of Terminations20
- Terminal Finish
Terminal Finish refers to the surface treatment applied to the terminals or leads of electronic components to enhance their performance and longevity. It can improve solderability, corrosion resistance, and overall reliability of the connection in electronic assemblies. Common finishes include nickel, gold, and tin, each possessing distinct properties suitable for various applications. The choice of terminal finish can significantly impact the durability and effectiveness of electronic devices.
Nickel/Palladium/Gold (Ni/Pd/Au) - Additional Feature
Any Feature, including a modified Existing Feature, that is not an Existing Feature.
WITH DIRECTION CONTROL - Voltage - Supply
Voltage - Supply refers to the range of voltage levels that an electronic component or circuit is designed to operate with. It indicates the minimum and maximum supply voltage that can be applied for the device to function properly. Providing supply voltages outside this range can lead to malfunction, damage, or reduced performance. This parameter is critical for ensuring compatibility between different components in a circuit.
2V~6V - Terminal Position
In electronic components, the term "Terminal Position" refers to the physical location of the connection points on the component where external electrical connections can be made. These connection points, known as terminals, are typically used to attach wires, leads, or other components to the main body of the electronic component. The terminal position is important for ensuring proper connectivity and functionality of the component within a circuit. It is often specified in technical datasheets or component specifications to help designers and engineers understand how to properly integrate the component into their circuit designs.
DUAL - Terminal Form
Occurring at or forming the end of a series, succession, or the like; closing; concluding.
GULL WING - Peak Reflow Temperature (Cel)
Peak Reflow Temperature (Cel) is a parameter that specifies the maximum temperature at which an electronic component can be exposed during the reflow soldering process. Reflow soldering is a common method used to attach electronic components to a circuit board. The Peak Reflow Temperature is crucial because it ensures that the component is not damaged or degraded during the soldering process. Exceeding the specified Peak Reflow Temperature can lead to issues such as component failure, reduced performance, or even permanent damage to the component. It is important for manufacturers and assemblers to adhere to the recommended Peak Reflow Temperature to ensure the reliability and functionality of the electronic components.
260 - Number of Functions1
- Supply Voltage
Supply voltage refers to the electrical potential difference provided to an electronic component or circuit. It is crucial for the proper operation of devices, as it powers their functions and determines performance characteristics. The supply voltage must be within specified limits to ensure reliability and prevent damage to components. Different electronic devices have specific supply voltage requirements, which can vary widely depending on their design and intended application.
5V - Time@Peak Reflow Temperature-Max (s)
Time@Peak Reflow Temperature-Max (s) refers to the maximum duration that an electronic component can be exposed to the peak reflow temperature during the soldering process, which is crucial for ensuring reliable solder joint formation without damaging the component.
30 - Base Part Number
The "Base Part Number" (BPN) in electronic components serves a similar purpose to the "Base Product Number." It refers to the primary identifier for a component that captures the essential characteristics shared by a group of similar components. The BPN provides a fundamental way to reference a family or series of components without specifying all the variations and specific details.
74HC245 - Pin Count
a count of all of the component leads (or pins)
20 - Qualification Status
An indicator of formal certification of qualifications.
Not Qualified - Output Type
The "Output Type" parameter in electronic components refers to the type of signal or data that is produced by the component as an output. This parameter specifies the nature of the output signal, such as analog or digital, and can also include details about the voltage levels, current levels, frequency, and other characteristics of the output signal. Understanding the output type of a component is crucial for ensuring compatibility with other components in a circuit or system, as well as for determining how the output signal can be utilized or processed further. In summary, the output type parameter provides essential information about the nature of the signal that is generated by the electronic component as its output.
3-State - Supply Voltage-Max (Vsup)
The parameter "Supply Voltage-Max (Vsup)" in electronic components refers to the maximum voltage that can be safely applied to the component without causing damage. It is an important specification to consider when designing or using electronic circuits to ensure the component operates within its safe operating limits. Exceeding the maximum supply voltage can lead to overheating, component failure, or even permanent damage. It is crucial to adhere to the specified maximum supply voltage to ensure the reliable and safe operation of the electronic component.
6V - Supply Voltage-Min (Vsup)
The parameter "Supply Voltage-Min (Vsup)" in electronic components refers to the minimum voltage level required for the component to operate within its specified performance range. This parameter indicates the lowest voltage that can be safely applied to the component without risking damage or malfunction. It is crucial to ensure that the supply voltage provided to the component meets or exceeds this minimum value to ensure proper functionality and reliability. Failure to adhere to the specified minimum supply voltage may result in erratic behavior, reduced performance, or even permanent damage to the component.
2V - Load Capacitance
the amount of capacitance measured or computed across the crystal terminals on the PCB. Frequency Tolerance. Frequency tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from nominal, in parts per million (PPM), at a specific temperature, usually +25°C.
50pF - Number of Ports
A port is identified for each transport protocol and address combination by a 16-bit unsigned number,.
2 - Family
In electronic components, the parameter "Family" typically refers to a categorization or classification system used to group similar components together based on their characteristics, functions, or applications. This classification helps users easily identify and select components that meet their specific requirements. The "Family" parameter can include various subcategories such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, integrated circuits, and more. Understanding the "Family" of an electronic component can provide valuable information about its compatibility, performance specifications, and potential uses within a circuit or system. It is important to consider the "Family" parameter when designing or troubleshooting electronic circuits to ensure proper functionality and compatibility with other components.
HC/UH - Logic Type
Logic Type in electronic components refers to the classification of circuits based on the logical operations they perform. It includes types such as AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR, each defining the relationship between binary inputs and outputs. The logic type determines how the inputs affect the output state based on specific rules of Boolean algebra. This classification is crucial for designing digital circuits and systems, enabling engineers to select appropriate components for desired functionalities.
Transceiver, Non-Inverting - Output Polarity
Output polarity in electronic components refers to the orientation of the output signal in relation to the ground or reference voltage. It indicates whether the output voltage is positive or negative with respect to the ground. Positive output polarity means the signal is higher than the ground potential, while negative output polarity signifies that the signal is lower than the ground. This characteristic is crucial for determining compatibility with other components in a circuit and ensuring proper signal processing.
TRUE - Number of Bits per Element8
- Height Seated (Max)
Height Seated (Max) is a parameter in electronic components that refers to the maximum allowable height of the component when it is properly seated or installed on a circuit board or within an enclosure. This specification is crucial for ensuring proper fit and alignment within the overall system design. Exceeding the maximum seated height can lead to mechanical interference, electrical shorts, or other issues that may impact the performance and reliability of the electronic device. Manufacturers provide this information to help designers and engineers select components that will fit within the designated space and function correctly in the intended application.
2.65mm - Width7.5mm
- RoHS Status
RoHS means “Restriction of Certain Hazardous Substances” in the “Hazardous Substances Directive” in electrical and electronic equipment.
ROHS3 Compliant
74HC245 Alternatives

74HC245 Functional Block Diagram

Logic Symbol

IEC Logic Symbol
Where to use 74HC245?
The 74HC245 is an 8-bit transceiver IC with 3-state output. Meaning it has two set of pins (A0-A7 and B0-B7), in which each set has 8 pins. Out of these two sets one set can be used as input and the other set can be used as output. Since the IC is a transceiver IC, Data can flow from input bus to output bus and also from output bus to input bus, by simply toggling the Direction pin (DIR) pin as required. It also has a decent output current of 35mA and hence can be used to drive nominal loads.
So if you are looking for an IC to act as a buffer or as a transceiver for your address or data bus. Or if you are looking for an IC to act as a 8-bit logic level converter then 74HC245 IC might be the right choice for you. It is also possible to use this IC for establishing communication protocol buses (SPI, IIC etc) between two different MCU/MPU with different operating voltages since the IC has high speed buffer. The 3 State at which 74HC245 IC can operate is shown in the table, the pins OE and DIR can be used as follows to set the state.

How to use 74HC245?
74HC245 IC has a vast application; however for simplicity let us consider we are using the IC to act as logic level converter. Many hardware like Raspberry Pi, MSP430 operates with a voltage of 3.3V, but other sensors or IC’s like Ultrasonic sensor, TFT LCD displays etc operate in 5V. So in these cases we have to shift one set of operating voltage (3.3V) to another set (5V). In these cases we employ a logic level converter; the simplest logic level converter is a potential divider. But it is not efficient for high speed operation or for bi-directional communication buses. Hence in those cases a bi-directional transceiver IC like 74HC245 seems to be an ideal choice.

A general circuit diagram using IC 74HC245 as a logic level converter is shown above. Here we are converting the 3.3V data lines to 5V data Lines. The Data can be made to flow in both the directions by controlling the DIR (AB/BA) as shown in the table above. Also we can reduce the input leakage current by disabling the inputs by using the OE pin as shown in the table above. The output voltage will always be equal to the Vcc voltage, so here since we are converting the 3.3V to 5V we should power the Vcc pin with +5V as shown above.
74HC245 Applications
-Used in addressing bus buffers
-Used in data bus transceivers
-Used in Logic level converters
-Used in driver IC for communication protocols
-Used in personal computers, PC' s and notebooks
-Used in servers
-Used in wearable health devices
-Used in fitness devices
-Used in telecom infrastructures
74HC245 Package

74HC245 Manufacturer
Nexperia is a global semiconductor manufacturer headquartered in Nijmegen, the Netherlands. It has front-end factories in Hamburg, Germany and Greater Manchester, England. It is the former Standard Products business unit of NXP Semiconductors (previously as Philips Semiconductors). The company's product range includes bipolar transistors, diodes, ESD protection, TVS diodes, MOSFETs, and logic devices.
Trend Analysis
Datasheet PDF
- PCN Packaging :
- Datasheets :
- PCN Assembly/Origin :
- PCN Design/Specification :
- RohsStatement :
Parts with Similar Specs
- ImagePart NumberManufacturerPackage / CaseNumber of PinsNumber of ElementsNumber of Bits per ElementSupply VoltageRoHS StatusOutput TypeNumber of PortsView Compare
74HC245D,653
20-SOIC (0.295, 7.50mm Width)
20
1
8
5 V
ROHS3 Compliant
3-State
2
14-SOIC (0.154, 3.90mm Width)
14
-
1
3.3 V
ROHS3 Compliant
3-State
2
20-SOIC (0.295, 7.50mm Width)
-
1
8
5 V
ROHS3 Compliant
3-State
2
20-SOIC (0.295, 7.50mm Width)
-
1
8
5 V
ROHS3 Compliant
3-State
2
14-SOIC (0.209, 5.30mm Width)
14
4
1
5 V
ROHS3 Compliant
3-State
2
1.What is the uses of 74HC245?
74HC245 is an eight-way buffer with controllable direction, which is mainly used to realize the two-way asynchronous communication of the data bus. In order to protect the fragile main control chip, a buffer is usually added between the parallel interface of the main control chip and the parallel interface of the external controlled device. When the main control chip and the controlled device need to realize two-way asynchronous communication, it is natural to choose a two-way eight-way buffer. 245 is for this kind of demand. It is common on the interfaces of parallel port LCD screens, parallel port printers, parallel port sensors or communication modules.
2.What is the difference between 74HC245 and 74HC573?
74HC245 is an eight-phase three-state transceiver, 74HC573 is an 8-bit three-state latch. Both have the function of latching a three-bit binary number, but the 74HC245 has the functions of two-way transmission and two-way latching, and the 74HC573 can only be one-way transmission and one-way latching.
3.Can 74HC245 replace 74HCT245?
It can be substituted in some cases. 74HC series devices have a wide operating voltage range (2V~6V), which is its advantage, but when used at the same voltage (5V) as 74HCT series devices, the specifications for input high and low levels are higher than 74HCT Series devices, so 74HCT series devices have better anti-interference performance.
 AT89S52-24PU Microcontroller: Diagram, Pinout, and Datasheet
AT89S52-24PU Microcontroller: Diagram, Pinout, and Datasheet04 March 20227453
 Analog Devices AD8065ARTZ-R2: Key Features and Applications
Analog Devices AD8065ARTZ-R2: Key Features and Applications28 May 2025776
 IRF520 MOSFET: Pinout, Datasheet, Test Circuit, and Equivalents
IRF520 MOSFET: Pinout, Datasheet, Test Circuit, and Equivalents31 July 202116156
 A Comparison Article about L293D & ULN2003
A Comparison Article about L293D & ULN200325 April 20227099
 2SC5198 NPN Transistor: Replacement, Circuit and Datasheet
2SC5198 NPN Transistor: Replacement, Circuit and Datasheet23 October 20219005
 AOZ1282CI 1.2A Simple Buck Regulator, AOZ1282CI Datasheet and Replacements
AOZ1282CI 1.2A Simple Buck Regulator, AOZ1282CI Datasheet and Replacements10 February 20222363
 TBA820M Amplifier: Datasheet, Circuit, Alternative
TBA820M Amplifier: Datasheet, Circuit, Alternative28 October 20215799
 A Comprehensive Guide to Fairchild 74ACTQ16245SSC Bus Transceiver
A Comprehensive Guide to Fairchild 74ACTQ16245SSC Bus Transceiver11 March 2024456
 Toroidal transformer: Principles, Features, Types and Applications
Toroidal transformer: Principles, Features, Types and Applications13 November 20208749
 Designing a GaN-based Dual Active Bridge for PHEV Chargers
Designing a GaN-based Dual Active Bridge for PHEV Chargers17 May 20242332
 RTD Sensors: Working Principle, Features and Applications
RTD Sensors: Working Principle, Features and Applications22 May 202512794
 What is an Integrated Circuit (ICs) and Why Integrated Circuit is shortage?
What is an Integrated Circuit (ICs) and Why Integrated Circuit is shortage?23 September 20217306
 Challenges and Issues in Smart Grid Infrastructure
Challenges and Issues in Smart Grid Infrastructure11 May 20234068
 Photocoupler Basis: Description, Applications and Working Principle
Photocoupler Basis: Description, Applications and Working Principle29 September 202110015
 Chiplet Brings Change to the Business Model of IP Design Companies
Chiplet Brings Change to the Business Model of IP Design Companies05 September 20224157
 GaN-Based liquid-level UVsensors for Direct and Continuous Measurement
GaN-Based liquid-level UVsensors for Direct and Continuous Measurement10 May 20232207
Nexperia USA Inc.
In Stock: 1436
United States
China
Canada
Japan
Russia
Germany
United Kingdom
Singapore
Italy
Hong Kong(China)
Taiwan(China)
France
Korea
Mexico
Netherlands
Malaysia
Austria
Spain
Switzerland
Poland
Thailand
Vietnam
India
United Arab Emirates
Afghanistan
Åland Islands
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antigua & Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba
Bosnia & Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
Christmas Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo
Congo (DRC)
Cook Islands
Costa Rica
Côte d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curaçao
Cyprus
Czechia
Denmark
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia
Georgia
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Honduras
Hungary
Iceland
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Jamaica
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macao(China)
Madagascar
Malawi
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Myanmar
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Korea
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Palestinian Authority
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Réunion
Romania
Rwanda
Samoa
San Marino
São Tomé & Príncipe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
South Sudan
Sri Lanka
St Helena, Ascension, Tristan da Cunha
St. Barthélemy
St. Kitts & Nevis
St. Lucia
St. Martin
St. Pierre & Miquelon
St. Vincent & Grenadines
Sudan
Suriname
Svalbard & Jan Mayen
Sweden
Syria
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad & Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks & Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
U.S. Outlying Islands
U.S. Virgin Islands
Uganda
Ukraine
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Vatican City
Venezuela
Wallis & Futuna
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe


 Product
Product Brand
Brand Articles
Articles Tools
Tools







