Best 1N4007 diode alternatives to use in 2025
You have many choices when you want a replacement for the 1n4007 diode. Here are five top alternatives for 2025:
UF4007 – Ultra-fast switching speed for better efficiency.
1N5819 Schottky diode – Lower voltage drop, ideal for power-saving designs.
1N5408 – Handles higher current, perfect for power circuits.
1N4148 – Fast switching for signal processing.
1N5817/1N5818 Schottky diodes – Great for low-voltage, high-frequency uses.
Today, you see the 1n4007 diode widely used in power supplies, LED lighting, and automotive electronics. The global diode market keeps growing, with new trends like energy-efficient materials and advanced schottky diode designs. These replacement diodes help you keep up with the latest technology and demands.
1N4007 Diode Alternatives
UF4007 Ultra-Fast Diode
You may want a diode that switches much faster than the 1n4007 diode. The UF4007 is an ultrafast recovery diode. It works well in circuits where you need quick switching, such as in switching power supplies or high-frequency rectifiers. The UF4007 reduces switching losses and heat, making your designs more efficient. If you work with modern electronics that demand speed, this diode is a strong choice. You can use it as a direct replacement for the 1n4007 diode in most cases, but you get better performance in fast-switching circuits.
1N5819 Schottky Diode
If you want to save power and reduce heat, the 1n5819 schottky diode is a great option. This schottky diode has a much lower forward voltage drop than the 1n4007 diode. When you use the 1n5819 schottky diode, your circuit loses less energy as heat. It also switches much faster, which helps in high-frequency circuits like DC-DC converters and switch-mode power supplies.
Tip: The 1n5819 schottky diode is best for low-voltage, high-speed applications. It is not suitable for high-voltage circuits because its maximum reverse voltage is lower than the 1n4007 diode.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Performance Parameter | 1N5819 Schottky Diode | 1N4007 Standard Rectifier Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Forward Voltage Drop (Vf) | ~0.45V at 1A | ~1.1V at 1A |
| Reverse Recovery Time (trr) | Nanoseconds | Microseconds |
| Maximum Reverse Voltage (Vr) | 40V | 1000V |
| Switching Frequency | High (MHz range) | Low (kHz range) |
You will notice that the 1n5819 schottky diode offers much lower voltage drop and faster switching, which means less power loss and better efficiency. However, it cannot handle high voltages like the 1n4007 diode.
1N5408 High-Power Diode
If your project needs to handle more current, the 1N5408 is a strong alternative. This diode can carry up to 3A of continuous current, much more than the 1n4007 diode, which is rated for only 1A. The 1N5408 also handles large surge currents, making it reliable in circuits with high inrush or short bursts of high current.
| Diode Model | Maximum Average Forward Current | Peak Forward Surge Current |
|---|---|---|
| 1N5408 | 3A | 200A |
| 1N4007 | 1A | 30A |
You can use the 1N5408 in battery chargers, power supplies, and as a protection device. It works well in circuits up to 1000V and is best for low-frequency applications, such as mains rectification. If you need a diode for high-frequency switching, you should look for a fast recovery diode or an ultrafast recovery diode instead.
Note: The 1N5408 is not suitable for high-frequency circuits. For those, you should use a fast recovery diode like the UF5408.
1N4148 Fast Switching Diode
You may need a diode that switches very quickly for signal processing or digital logic. The 1N4148 is a popular choice for these tasks. It is a fast switching diode, making it ideal for circuits that need to respond to changes in voltage or current in a fraction of a microsecond.
You can use the 1N4148 in:
Signal rectification
Clamping circuits to protect sensitive parts
Logic gates in digital circuits
Reverse voltage protection
Current spike suppression
High-speed switching circuits
The 1N4148 comes in many package types, so you can use it in both prototypes and finished products. It is reliable, low-cost, and works well in many modern electronics.
1N5817/1N5818 Schottky Diodes
If you work with low-voltage, high-frequency circuits, the 1N5817 and 1N5818 schottky diodes are excellent alternatives. These diodes have a low forward voltage drop, usually around 0.4V, and switch very quickly. You can use them in power supplies, battery chargers, and high-frequency rectifiers where efficiency matters.
The 1N5817 and 1N5818 are best for circuits with a maximum output current of about 1A and a peak reverse voltage around 20V. They are not suitable for high-voltage applications, but they outperform the 1n4007 diode in speed and efficiency for low-voltage uses.
Tip: Choose these schottky diodes when you need fast switching and low power loss in your design.
Diode Comparison Table
Key Specs Overview
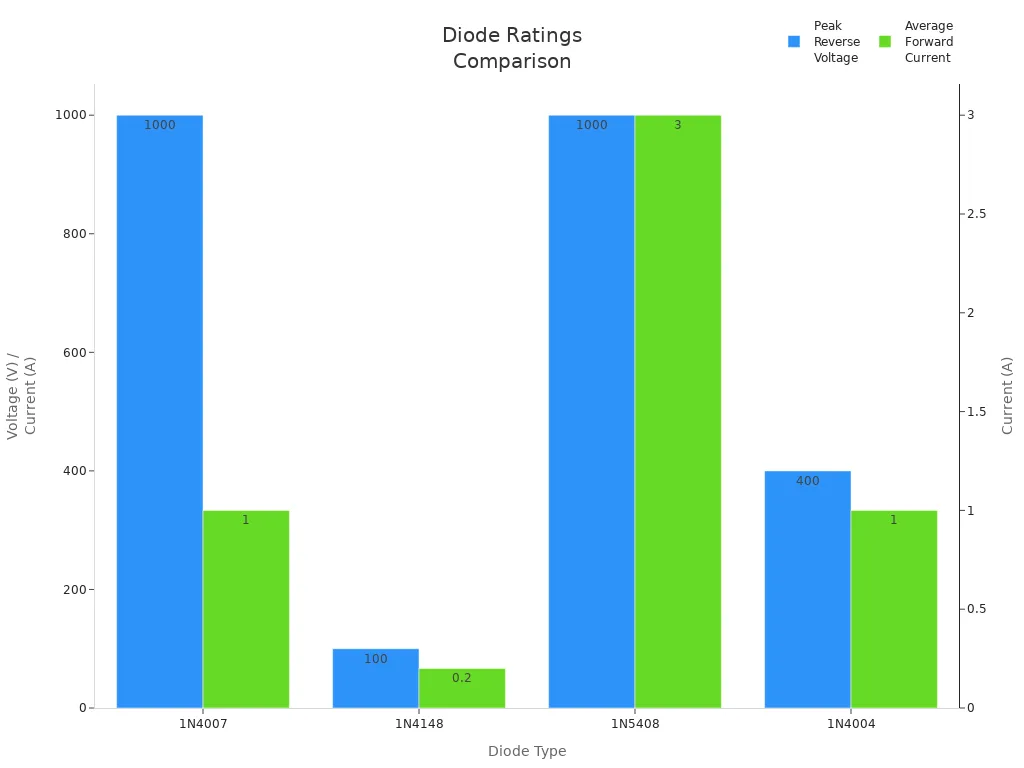
When you compare rectifier diodes, you need to look at several important features. These include reverse voltage, forward current, switching speed, package type, and price. The table below gives you a clear overview of how the 1n4007 diode and its top alternatives stack up:
| Diode Model | Reverse Voltage (V) | Forward Current (A) | Switching Speed | Package Type | Price (2025) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1N4007 | 1000 | 1 | Slow (~30 µs) | DO-41 | Moderate |
| UF4007 | 1000 | 1 | Fast (~75 ns) | DO-41 | Moderate |
| 1N5819 | 40 | 1 | Very Fast (ns) | DO-41/SMD | Moderate |
| 1N5408 | 1000 | 3 | Slow | DO-201 | Higher |
| 1N4148 | 100 | 0.2 | Very Fast (4 ns) | DO-35/SMD | Low |
| 1N5817/1N5818 | 20/30 | 1 | Very Fast (ns) | DO-41/SMD | Moderate |
Tip: Schottky rectifier diodes like 1N5819 and 1N5817 offer the lowest forward voltage drop, which helps you save power in your circuit.
You can see that each rectifier diode has strengths in different areas. For example, the 1N5408 handles the highest current, while the 1N4148 and Schottky diodes switch the fastest.
1N4007 vs Alternatives
You want to know where each rectifier diode excels compared to the 1n4007 diode. Here is a quick breakdown:
Reverse Voltage: The 1n4007 diode leads with a 1000V rating. Only the UF4007 and 1N5408 match this, making them best for high-voltage rectifier circuits.
Current Handling: The 1N5408 stands out. It can handle 3A, which is three times more than the 1n4007 diode. This makes it ideal for power rectifier applications.
Switching Speed: The UF4007, 1N4148, and Schottky rectifier diodes (1N5819, 1N5817, 1N5818) switch much faster than the 1n4007 diode. You should pick these for high-frequency or fast recovery diode needs.
Forward Voltage Drop: Schottky rectifier diodes like 1N5819 and 1N5817 have the lowest voltage drop, usually around 0.4V. This helps you reduce heat and save energy.
Package Type: Most rectifier diodes come in DO-41 or similar packages. The 1N5408 uses a larger DO-201 package for higher current. SMD versions are available for compact designs.
Price: The 1n4007 diode and its alternatives are all affordable. The 1N4148 is usually the cheapest. The 1N5408 costs more due to its higher current rating.
If you need a rectifier for high voltage, stick with the 1n4007 diode, UF4007, or 1N5408. For fast switching, choose a fast recovery diode like the UF4007 or a Schottky rectifier diode. For high current, the 1N5408 is your best bet.
You can now match the right rectifier diode to your project by checking these specs. This helps you build safer, more efficient circuits.
Choosing a Diode
Selection Factors
When you select a diode for your project, you need to match its features to your circuit’s needs. The right choice keeps your electronics safe and efficient. Here are the most important factors to consider:
| Factor | Why It Matters | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage rating | Prevents breakdown from high reverse voltage | AC mains rectifiers |
| Current rating | Handles the maximum current without overheating | Battery chargers |
| Forward voltage drop | Reduces power loss and heat | Low-voltage, high-efficiency circuits |
| Reverse recovery time | Improves switching speed and efficiency | High-frequency switching supplies |
| Power dissipation | Ensures the diode can handle heat | Power supply rectification |
| Thermal resistance | Helps manage heat in compact designs | Small PCB layouts |
| Surge current rating | Protects against short bursts of high current | Circuits with inrush or high surge protection |
| Diode type | Matches performance to your application | Schottky for speed, rectifier for power |
Tip: Always choose a diode with voltage and current ratings higher than your circuit’s maximum values. This gives you a safety margin for unexpected surges.
Example Scenarios
You can use these examples to help pick the best diode for your needs:
High-Frequency Switching:
If you build a switching power supply or work with 5G or IoT devices, use a fast switching diode like the UF4007 or 1N4148. These diodes have short reverse recovery times, which means less energy loss and better efficiency.Power Supply Rectification:
For circuits that convert AC to DC, such as laptop chargers or industrial equipment, choose a robust rectifier diode like the 1N4007 or 1N5408. If you need even better performance, consider new GaN or SiC diodes. These handle higher voltages, higher temperatures, and switch faster than traditional silicon diodes.Low-Voltage, High-Efficiency Circuits:
In battery-powered or portable devices, Schottky diodes like the 1N5819 or 1N5817 work best. Their low forward voltage drop saves power and reduces heat, making your design more efficient.Circuits with High Surge Protection Needs:
If your circuit faces inrush currents, such as when turning on motors or charging capacitors, select a diode with a high surge current rating. The 1N5408 is a good choice for these situations.
Remember, always check the availability and cost of your chosen diode. Some advanced types may cost more or be harder to find, but they can offer big benefits for modern electronics.
You have many strong options when replacing the 1N4007. The table below highlights how each alternative meets modern electronics needs:
| Diode Alternative | Main Strengths in Modern Electronics |
|---|---|
| 1N4004 | Reliable for circuits under 400V, optimized for lower voltage needs |
| 1N4005 | Balances voltage capacity and reliability up to 600V |
| 1N4006 | Handles up to 800V, robust for higher voltage demands |
| HER158, HER208, FR107, FR207 | Dependable at 800V–1000V, ideal for elevated voltage conditions |
| EM51, 1N5399, EM52 | Durable at 1000V, suitable for high voltage and current |
When you choose a diode, always check voltage, current, and surge ratings. Avoid common mistakes like mismatching direction or ignoring surge requirements:
Selecting a diode with low surge ratings can cause failure.
Failing to match surge protection to your circuit may damage devices.
Stay updated on trends by reading market reports or joining forums like EE Times. Share your experiences or questions in the comments to help others find the best solution.
FAQ
What makes the UF4007 a better choice for fast switching?
You get much faster switching with the UF4007. This diode works well in circuits that need quick response times. You can use it in high-frequency power supplies or digital circuits where speed matters.
Can I use a Schottky diode instead of the 1N4007?
You can use a Schottky diode if your circuit runs at low voltage and needs high efficiency. Schottky diodes have a lower voltage drop and switch faster. They do not work well in high-voltage circuits.
When should I pick the 1N5408 over the 1N4007?
You should pick the 1N5408 when your circuit needs to handle more current. The 1N5408 supports up to 3A. It works best in power supplies and battery chargers that need higher current.
Is the 1N4148 suitable for power rectification?
You should not use the 1N4148 for power rectification. This diode is best for signal processing and fast switching. It cannot handle high current like the 1N4007 or 1N5408.
 All You Need to Know About Rectifier CircuitUTMEL24 April 202513877
All You Need to Know About Rectifier CircuitUTMEL24 April 202513877All You Need to Know About Rectifier Circuit
Read More 15 Key Elements of Diode SelectionUTMEL26 November 202116025
15 Key Elements of Diode SelectionUTMEL26 November 202116025Hello everyone, I am Rose. Welcome back to the new post today. Diodes are one of the most common components in our circuit boards. So, what factors should be considered when selecting models?
Read More What is a PIN Diode?UTMEL04 February 20218790
What is a PIN Diode?UTMEL04 February 20218790While diodes with a simple PN junction are by far the most common type of diode in operation, in a variety of applications, other forms of diode may be used. The PIN diode is one type that is used for a number of circuits. In a variety of places, this diode type is used. For RF switching, the PIN diode is very fine, and the PIN structure in photodiodes is very useful as well.
Read More Microwave Diode: Introduction and TypesUTMEL07 January 202121654
Microwave Diode: Introduction and TypesUTMEL07 January 202121654Microwave diodes are diodes that work in the microwave frequency band. It is a solid-state microwave device. Microwave band usually refers to the frequency from 300 MHz to 3000 GHz. After the discovery of the point contact diode effect at the end of the 19th century, microwave diodes such as PIN diodes, varactor diodes, and Schottky diode tubes appeared one after another. Microwave diodes have the advantages of small size and high reliability, and are used in microwave oscillation, amplification, frequency conversion, switching, phase shifting and modulation.
Read More What Determines the Maximum Operating Frequency of a Diode?UTMEL29 June 202211315
What Determines the Maximum Operating Frequency of a Diode?UTMEL29 June 202211315Hello, wish you a wonderful day. In this essay, we first pose the following query: what determines the diode's maximum operating frequency? In regards to the solution, the first thing we need to understand is that the junction capacitance and the reverse recovery time of the diode are two distinct concepts. The charging and discharging times of the junction capacitance cannot match the reverse recovery time. You say that, why? Let's start by taking a look at these facts.
Read More
Subscribe to Utmel !
![35F0121-0SR-10]() 35F0121-0SR-10
35F0121-0SR-10Laird-Signal Integrity Products
![BLM15BD750SN1D]() BLM15BD750SN1D
BLM15BD750SN1DMurata Electronics
![BLM18KG102SH1D]() BLM18KG102SH1D
BLM18KG102SH1DMurata Electronics
![BLA31AG221SN4D]() BLA31AG221SN4D
BLA31AG221SN4DMurata Electronics
![HFCN-1100]() HFCN-1100
HFCN-1100Mini-Circuits
![SCLF-4.7]() SCLF-4.7
SCLF-4.7Mini-Circuits
![BLM41AF151SN1L]() BLM41AF151SN1L
BLM41AF151SN1LMurata Electronics
![BK1608HM601-T]() BK1608HM601-T
BK1608HM601-TTaiyo Yuden
![BK2125LM252-T]() BK2125LM252-T
BK2125LM252-TTaiyo Yuden
![742792063]() 742792063
742792063Würth Elektronik












