onsemi BC557C Transistor Top Uses for Electronics
TRANS PNP 45V 0.1A TO-92
onsemi BC557C excels in audio amplifiers, switching, LED drivers, sensor modules, and preamps for reliable 2025 electronics circuit design.
Product Introduction
If you love building circuits, the onsemi bc557c is a transistor you’ll want to keep around. You can use this transistor for many tasks. Here are the top 5 common applications for the bc557:
Amplifiers for audio or small radios
Switches in low-power circuits
LED drivers
Sensor modules
Audio preamps
The bc557 works well for students, engineers, or anyone learning about electronics. You’ll see the onsemi bc557c in many modern circuits because it’s reliable. Try these applications in your next project and see what this transistor can do!
onsemi bc557c Overview
Features
When you look at the onsemi bc557c, you see a small but powerful part. This transistor is a PNP type, which means it works well for many low-power circuits. You can use the bc557 in audio projects, sensor circuits, and even as a switch. The bc557 has a TO-92 package, so it fits easily on most breadboards and PCBs.
Here’s a quick look at what makes the onsemi bc557c stand out:
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Transistor Type | PNP Bipolar Junction |
| Package | TO-92 (3 pins) |
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage | 45 V |
| Maximum Collector-Base Voltage | 50 V |
| Maximum Emitter-Base Voltage | -5 V |
| Maximum Collector Current | -100 mA |
| Power Dissipation | 625 mW |
| Minimum DC Current Gain (hFE) | 800 @ -2 mA |
| Max Collector-Emitter Saturation Voltage | 0.075 V @ 10 mA |
| Max Base-Emitter Saturation Voltage | -0.7 V @ 10 mA |
| Maximum Operating Frequency | 320-360 MHz |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55°C to 150°C |
| Physical Dimensions (W x H x L) | ~4.7 mm x 4.56 mm x 4.7 mm |
| Mounting Type | Through Hole |
You get a high current gain, which means the bc557 can amplify weak signals. The maximum collector current is -100 mA, so you can drive small loads like LEDs or buzzers. The power dissipation of 625 mW lets you use the transistor in circuits that need a bit more power. The bc557 also works at high frequencies, up to 360 MHz, which is great for radio and audio projects.
Popularity
You might wonder why so many people choose the onsemi bc557c for their projects. The answer is simple: it offers better specs than most other PNP transistors in its class. The bc557 gives you a higher minimum DC current gain, lower saturation voltage, and higher power dissipation. You also get a wide temperature range, so your circuits stay stable in different environments.
Check out this chart to see how the bc557 stacks up against a typical PNP transistor:
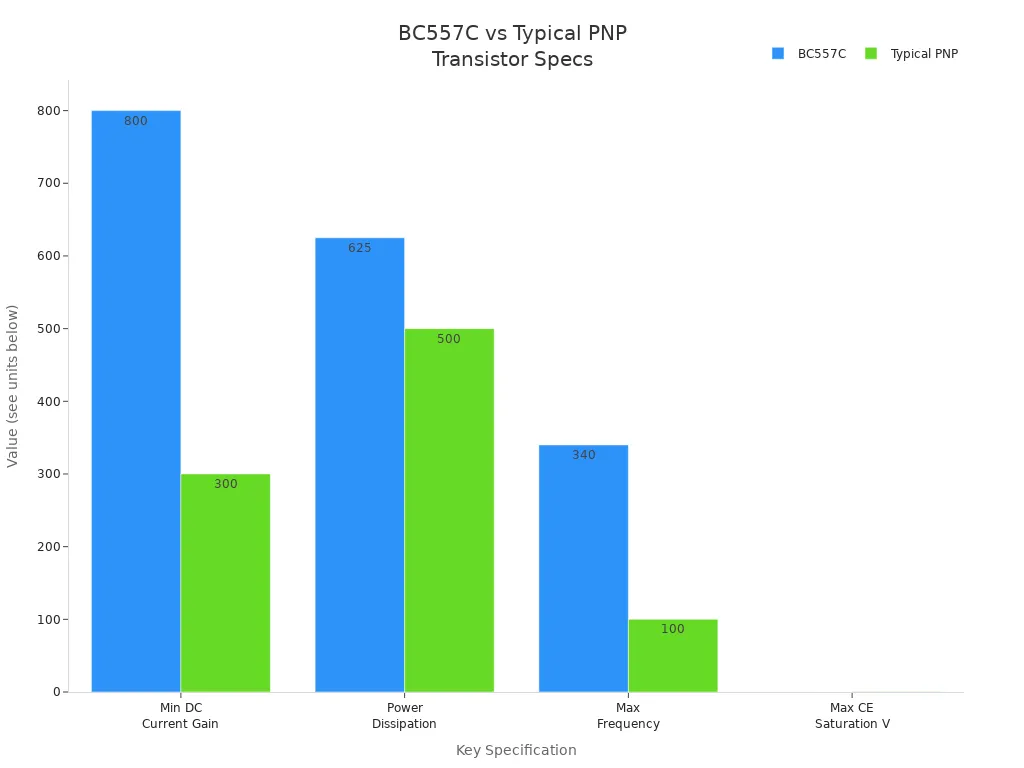
You can see that the bc557 outperforms many similar parts. That’s why you find this transistor in so many kits and projects. If you want a reliable and flexible bipolar junction transistor, the onsemi bc557c is a smart choice. You can use it for switching, amplification, and more. Many hobbyists and engineers trust the bc557 because it works well and lasts a long time.
Tip: If you’re just starting with electronics, try using the bc557 in your first amplifier or sensor circuit. You’ll see how easy it is to get good results with this transistor.
bc557 applications
The bc557 transistor gives you a lot of options when you build circuits. You can use it for many different applications. Let’s look at three of the most popular ways you can use the bc557 in your projects.
Amplification
You can use the bc557 transistor for amplification in many circuits. This means you can make weak signals stronger. If you build an audio amplifier, the bc557 helps boost the sound from a small radio or a buzzer. You can also use it in microphone preamps. The high current gain of the bc557 makes it perfect for these applications. You get clear sound and better volume without much noise.
Here are some common amplification applications for the bc557:
Small audio amplifiers for radios and speakers
Buzzers that need a louder output
Microphone preamplifiers for better sound pickup
Tip: Try using the bc557 transistor in a simple audio amplifier circuit. You will notice how much louder and clearer your sound becomes.
Switching
The bc557 transistor works great as a switch in low-power circuits. You can use it to turn devices on and off, like LEDs or small motors. The bc557 handles collector currents up to 100mA, so it fits well in many switching applications. It also has a high DC current gain, which means it switches with little effort from your control signal.
The bc557 is very efficient in switching roles. It does not waste much power, so your circuit stays cool and lasts longer. The transistor also switches quickly. With a transition frequency of about 100 MHz, you get fast response times. This makes the bc557 perfect for logic control, timers, and sensor circuits. You can trust it to activate and deactivate loads right when you need.
Here are some switching applications for the bc557:
Logic gates and digital control circuits
Timers that need fast switching
Turning on and off small loads like buzzers or relays
Note: The bc557 transistor’s low saturation voltage and thermal stability help your circuits run smoothly and reliably.
LED Drivers
You can use the bc557 transistor as an LED driver in many projects. It lets you control one or more LEDs with a small input signal. The bc557 can handle the current needed for most standard LEDs. You can also use it to make a constant current source, which keeps your LEDs bright and steady.
Here’s a simple table showing how you might use the bc557 in LED driver applications:
| Application | What the bc557 Does | Why Use It? |
|---|---|---|
| LED On/Off Control | Acts as a switch | Easy to control with logic |
| LED Brightness Control | Regulates current | Keeps LEDs safe and bright |
| LED Arrays | Drives multiple LEDs | Handles small loads easily |
You can build LED indicators, displays, or even simple light shows with the bc557. The transistor’s high gain and low power loss make it a smart choice for these applications.
Try this: Connect the bc557 to a microcontroller output. You can then control several LEDs with just one pin!
The bc557 transistor stands out because it fits so many applications. You can use it for amplification, switching, and as an LED driver. This makes it a favorite for hobbyists and engineers who want reliable and flexible parts in their circuits.
Sensor and Imaging Applications
When you explore sensor and imaging circuits, you will see the bc557 transistor pop up in many places. This little part helps you build smarter and more sensitive devices. Let’s look at how you can use the bc557 in different sensor applications.
Image Sensors
You might wonder how cameras and scanners pick up light and turn it into signals. The bc557 transistor plays a big role here. You can use this transistor to amplify the tiny signals that image sensors create. When light hits the sensor, it makes a weak current. The bc557 boosts this current so your circuit can process the image. You get clearer pictures and better detail because the transistor helps the sensor work at its best.
Tip: Try using the bc557 in a simple camera module project. You will see how much it improves the signal from the sensor.
Photodetectors
Photodetectors sense light and turn it into electrical signals. You can use the bc557 transistor to make these signals strong enough for your microcontroller or display. The transistor acts like a bridge between the weak output of the photodetector and the rest of your circuit. This makes your light-sensing applications more reliable. You can use the bc557 in light meters, automatic night lights, or even simple solar trackers.
Here’s a quick table showing common photodetector applications for the bc557:
| Application | Role of bc557 transistor |
|---|---|
| Light meters | Amplifies sensor output |
| Night lights | Switches LEDs on/off |
| Solar trackers | Boosts signal for control |
ISPs
Image Signal Processors (ISPs) need clean and strong signals from sensors. The bc557 transistor helps you get those signals. You can use this transistor to filter noise and stabilize the current before it reaches the ISP. This means your images look sharper and your circuits run smoother. The bc557 works well in these applications because it handles small signals with high gain.
You will find the bc557 in many sensor modules and imaging circuits. This transistor gives you the flexibility to design better and more reliable electronics. If you want to build smart cameras, light sensors, or imaging tools, the bc557 is a great choice.
bc557 transistor in Audio Circuits
Audio Amplifiers
You might want your music or voice to sound clear and strong. The bc557 transistor helps you do that. Many people use this transistor in audio amplifiers because it gives you high-fidelity sound. You can find the bc557 in famous designs like the garAM10BC and other gar series audio amplifiers. If you ever need to replace an old BC560C, you can use the bc557 transistor without changing your circuit. This makes repairs and upgrades easy.
The bc557 works well in both class-A and class-AB audio amplifiers. You often see it in mirrored differential pairs, cascode, or follower setups. These setups help your amplifier handle high frequencies and keep the current balanced. When you use the bc557 transistor, you get less distortion and better sound, even at low bass levels. People say the sound is clean and smooth, almost like a high-end valve amplifier. You will notice that your music has more detail and less noise.
Tip: If you want to build your own small-signal amplifier, try using the bc557 transistor in the input stage. You will hear the difference in audio quality.
Preamplifiers
Preamplifiers and audio recording circuits need to boost weak signals before sending them to speakers or other devices. The bc557 transistor is perfect for this job. It gives you high gain, which means it can make small sounds much louder. At the same time, it keeps noise low, so your recordings stay clear.
Here’s a table that shows why the bc557 transistor works so well in preamplifiers and audio recording:
| Feature | What It Means for You |
|---|---|
| High DC Current Gain | Louder, clearer sound |
| Low Noise | Less hiss and unwanted interference |
| Good Frequency Response | Works well for music and voice |
| Low Power Consumption | Stays cool and saves energy |
When you use the bc557 in preamplifiers, you get strong, clean signals. This makes your audio recordings sound professional. The transistor controls a larger current with a small base current, so you get more gain without extra heat or distortion. If you want your preamplifiers and audio recording projects to sound their best, the bc557 transistor is a smart choice.
Note: The bc557 transistor is a favorite for both hobbyists and pros who want great audio amplification and reliable preamplifiers.
bc557 in Thermal and Ultrasonic Sensors
Thermal Management
You want your circuits to work well, even when the temperature changes. The bc557 transistor helps you do that. This little part stays stable in hot or cold places. You can use the bc557 in sensor circuits that need to handle tough environments. If you build a temperature sensor or a fan controller, the bc557 keeps your readings steady.
Here’s a quick table to show you the best conditions for the bc557 transistor in sensor projects:
| Parameter | Recommended Condition |
|---|---|
| Maximum Voltage | Below -45V DC |
| Load Current | Under 100 mA |
| Operating Temperature | -65°C to +150°C |
| Thermal Management | Use heatsinks, ensure proper ventilation, and strategic component placement |
You can see that the bc557 works in a wide range of temperatures. You just need to keep the voltage and current within safe limits. Good airflow and smart placement help the bc557 transistor last longer. If you follow these tips, your sensor circuits will run smoothly.
Tip: Place the bc557 away from heat sources and give it space to breathe. This helps your sensor modules stay accurate.
Ultrasonic Sensing
Ultrasonic sensors help you measure distance or detect objects. You find these sensors in robots, parking systems, and even some smart home devices. The bc557 transistor plays a key role in these modules. It can amplify the weak signals from the ultrasonic receiver. You also use the bc557 to switch the transmitter on and off.
When you use the bc557 in ultrasonic sensor circuits, you get fast and reliable response. The transistor handles quick pulses and keeps the signal clean. You can trust the bc557 to work well, even if the temperature changes or the environment gets noisy.
Here’s how you might use the bc557 in an ultrasonic sensor module:
Amplify the echo signal from the receiver
Switch the transmitter circuit
Keep the sensor stable in different weather
The bc557 transistor gives you the flexibility to build sensors that work in many places. You can count on it for both thermal management and ultrasonic sensing. Try adding the bc557 to your next sensor project and see how much better your results can be!
Using the onsemi bc557c Effectively
Selection Tips
When you pick a bc557 transistor for your project, you want to make sure it fits your needs. Here are some things you should check:
Choose the right type. The bc557 is a PNP transistor, so use it where you need current to flow from emitter to collector.
Check the voltage and current ratings. The bc557 can handle up to 45V and 100mA. This works well for voltage regulation and small loads.
Look at the gain. The bc557C version has a high current gain, which is great for amplifiers and voltage regulation circuits.
Think about heat. If your circuit gets warm, add a heatsink or give the transistor space to cool down.
Make sure the transistor matches your application. The bc557 is good for switching, amplification, and even power supply circuits.
Tip: The bc557 is similar to the S9015 transistor. Both work well for low-power and voltage regulation tasks.
Connection Guide
Wiring the bc557 is easy if you follow a few steps. The pins are usually arranged as collector, base, and emitter. Always check the datasheet or use a multimeter to confirm the pinout.
Here’s a simple table to help you connect the bc557:
| Pin | Function | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Collector | Output | Connects to load |
| Base | Control | Connects to input signal |
| Emitter | Ground/+V | Connects to supply rail |
Double-check your connections. Mixing up the pins can stop your circuit from working.
Use the right base resistor. Calculate it with the formula:
Rb = (Vin - Vbe) / IbFor voltage regulation, make sure the bc557 is not overloaded.
Note: Always stay within the voltage and current limits to keep your bc557 safe.
Troubleshooting
Sometimes, things do not work as planned. Here are common problems and how you can fix them:
Wrong Pin Connections: If your circuit does not work, check the pinout. Use a multimeter to test each pin.
Overloading: If the bc557 gets hot or fails, you may have too much voltage or current. Stay below 45V and 100mA.
Improper Biasing: If you hear noise or see distortion, check your base resistor. Make sure the transistor is in the right region for voltage regulation.
Thermal Issues: If the transistor overheats, add a heatsink or move it away from other hot parts.
Circuit Design Flaws: Sometimes, the problem is in the design. For example, a base-emitter voltage drop can keep the transistor on all the time. Review your circuit and try using a different variant if needed.
Tip: If you need more gain for voltage regulation, use the bc557C version. For switching, other variants may work better.
With these tips, you can use the bc557 in many projects, from voltage regulation to power supply circuits. Careful selection, correct wiring, and smart troubleshooting will help your circuits run smoothly.
You’ve seen how the onsemi BC557C transistor fits into so many projects. Check out this quick table to remember its top uses:
| Application Area | Practical Value / Feature |
|---|---|
| Amplification Circuits | High gain, low noise, clear sound |
| Switching Applications | Fast switching, low voltage drop, great for digital circuits |
| LED Drivers & Constant Current | Steady LED control, stable current flow |
| Audio Circuits & Preamplifiers | Clean audio, excellent tone control |
| Power Supply & Voltage Reg. | Reliable voltage, thermal stability |
You can count on the BC557C for its balance of efficiency, precision, and durability. It stands out in low-power circuits and keeps your projects running smoothly, just like its close cousin, the BC556B. Want to learn more? Try these resources:
DigiKey’s articles and design tools
EEVblog’s electronics community forum
Keep experimenting and see what you can build next! 🚀
FAQ
What makes a bipolar junction transistor different from other types?
You use a bipolar junction transistor when you want to control current with another current. It works well for switching and amplification. Other types, like FETs, use voltage to control current. You often see BJTs in beginner projects.
Can I use the bc557 transistor for audio amplification?
Yes, you can! The bc557 transistor works great for audio amplification. It boosts weak signals from microphones or radios. You get clear sound with low noise. Many hobbyists use it in small-signal amplifier circuits.
Where do I find common applications for led drivers?
You find common applications for led drivers in indicator lights, displays, and backlighting. You can use a simple circuit with a transistor to control several LEDs at once. This setup keeps your LEDs bright and safe.
How does voltage regulation work in power supply circuits?
Voltage regulation keeps the output voltage steady in power supply circuits. You use a transistor to control the flow of current. This helps protect your devices from voltage spikes or drops. Many circuits use this method for safety.
Specifications
- TypeParameter
- Lifecycle Status
Lifecycle Status refers to the current stage of an electronic component in its product life cycle, indicating whether it is active, obsolete, or transitioning between these states. An active status means the component is in production and available for purchase. An obsolete status indicates that the component is no longer being manufactured or supported, and manufacturers typically provide a limited time frame for support. Understanding the lifecycle status is crucial for design engineers to ensure continuity and reliability in their projects.
LAST SHIPMENTS (Last Updated: 2 days ago) - Mounting Type
The "Mounting Type" in electronic components refers to the method used to attach or connect a component to a circuit board or other substrate, such as through-hole, surface-mount, or panel mount.
Through Hole - Package / Case
refers to the protective housing that encases an electronic component, providing mechanical support, electrical connections, and thermal management.
TO-226-3, TO-92-3 (TO-226AA) - Number of Pins3
- Supplier Device Package
The parameter "Supplier Device Package" in electronic components refers to the physical packaging or housing of the component as provided by the supplier. It specifies the form factor, dimensions, and layout of the component, which are crucial for compatibility and integration into electronic circuits and systems. The supplier device package information typically includes details such as the package type (e.g., DIP, SOP, QFN), number of pins, pitch, and overall size, allowing engineers and designers to select the appropriate component for their specific application requirements. Understanding the supplier device package is essential for proper component selection, placement, and soldering during the manufacturing process to ensure optimal performance and reliability of the electronic system.
TO-92-3 - Collector-Emitter Breakdown Voltage45V
- Collector-Emitter Saturation Voltage-300mV
- Current-Collector (Ic) (Max)100mA
- hFEMin420
- Operating Temperature
The operating temperature is the range of ambient temperature within which a power supply, or any other electrical equipment, operate in. This ranges from a minimum operating temperature, to a peak or maximum operating temperature, outside which, the power supply may fail.
-55°C~150°C TJ - Packaging
Semiconductor package is a carrier / shell used to contain and cover one or more semiconductor components or integrated circuits. The material of the shell can be metal, plastic, glass or ceramic.
Bulk - Published2005
- Part Status
Parts can have many statuses as they progress through the configuration, analysis, review, and approval stages.
Obsolete - Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL)
Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) is a standardized rating that indicates the susceptibility of electronic components, particularly semiconductors, to moisture-induced damage during storage and the soldering process, defining the allowable exposure time to ambient conditions before they require special handling or baking to prevent failures
1 (Unlimited) - Max Operating Temperature
The Maximum Operating Temperature is the maximum body temperature at which the thermistor is designed to operate for extended periods of time with acceptable stability of its electrical characteristics.
150°C - Min Operating Temperature
The "Min Operating Temperature" parameter in electronic components refers to the lowest temperature at which the component is designed to operate effectively and reliably. This parameter is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning and longevity of the component, as operating below this temperature may lead to performance issues or even damage. Manufacturers specify the minimum operating temperature to provide guidance to users on the environmental conditions in which the component can safely operate. It is important to adhere to this parameter to prevent malfunctions and ensure the overall reliability of the electronic system.
-55°C - Voltage - Rated DC
Voltage - Rated DC is a parameter that specifies the maximum direct current (DC) voltage that an electronic component can safely handle without being damaged. This rating is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning and longevity of the component in a circuit. Exceeding the rated DC voltage can lead to overheating, breakdown, or even permanent damage to the component. It is important to carefully consider this parameter when designing or selecting components for a circuit to prevent any potential issues related to voltage overload.
-45V - Max Power Dissipation
The maximum power that the MOSFET can dissipate continuously under the specified thermal conditions.
625mW - Current Rating
Current rating is the maximum current that a fuse will carry for an indefinite period without too much deterioration of the fuse element.
-100mA - Base Part Number
The "Base Part Number" (BPN) in electronic components serves a similar purpose to the "Base Product Number." It refers to the primary identifier for a component that captures the essential characteristics shared by a group of similar components. The BPN provides a fundamental way to reference a family or series of components without specifying all the variations and specific details.
BC557 - Polarity
In electronic components, polarity refers to the orientation or direction in which the component must be connected in a circuit to function properly. Components such as diodes, capacitors, and LEDs have polarity markings to indicate which terminal should be connected to the positive or negative side of the circuit. Connecting a component with incorrect polarity can lead to malfunction or damage. It is important to pay attention to polarity markings and follow the manufacturer's instructions to ensure proper operation of electronic components.
PNP - Element Configuration
The distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals.
Single - Power - Max
Power - Max is a parameter that specifies the maximum amount of power that an electronic component can handle without being damaged. It is typically measured in watts and indicates the upper limit of power that can be safely supplied to the component. Exceeding the maximum power rating can lead to overheating, malfunction, or permanent damage to the component. It is important to consider the power-max rating when designing circuits or systems to ensure proper operation and longevity of the electronic components.
625mW - Gain Bandwidth Product
The gain–bandwidth product (designated as GBWP, GBW, GBP, or GB) for an amplifier is the product of the amplifier's bandwidth and the gain at which the bandwidth is measured.
100MHz - Transistor Type
Transistor type refers to the classification of transistors based on their operation and construction. The two primary types are bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs). BJTs use current to control the flow of current, while FETs utilize voltage to control current flow. Each type has its own subtypes, such as NPN and PNP for BJTs, and MOSFETs and JFETs for FETs, impacting their applications and characteristics in electronic circuits.
PNP - Collector Emitter Voltage (VCEO)
Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) is a key parameter in electronic components, particularly in transistors. It refers to the maximum voltage that can be applied between the collector and emitter terminals of a transistor while the base terminal is open or not conducting. Exceeding this voltage limit can lead to breakdown and potential damage to the transistor. VCEO is crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the transistor within its specified limits. Designers must carefully consider VCEO when selecting transistors for a circuit to prevent overvoltage conditions that could compromise the performance and longevity of the component.
650mV - Max Collector Current
Max Collector Current is a parameter used to specify the maximum amount of current that can safely flow through the collector terminal of a transistor or other electronic component without causing damage. It is typically expressed in units of amperes (A) and is an important consideration when designing circuits to ensure that the component operates within its safe operating limits. Exceeding the specified max collector current can lead to overheating, degradation of performance, or even permanent damage to the component. Designers must carefully consider this parameter when selecting components and designing circuits to ensure reliable and safe operation.
100mA - DC Current Gain (hFE) (Min) @ Ic, Vce
The parameter "DC Current Gain (hFE) (Min) @ Ic, Vce" in electronic components refers to the minimum value of the DC current gain, denoted as hFE, under specific operating conditions of collector current (Ic) and collector-emitter voltage (Vce). The DC current gain hFE represents the ratio of the collector current to the base current in a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), indicating the amplification capability of the transistor. The minimum hFE value at a given Ic and Vce helps determine the transistor's performance and efficiency in amplifying signals within a circuit. Designers use this parameter to ensure proper transistor selection and performance in various electronic applications.
420 @ 2mA 5V - Current - Collector Cutoff (Max)
The parameter "Current - Collector Cutoff (Max)" refers to the maximum current at which a transistor or other electronic component will cease to conduct current between the collector and emitter terminals. This parameter is important in determining the maximum current that can flow through the component when it is in the cutoff state. Exceeding this maximum cutoff current can lead to malfunction or damage of the component. It is typically specified in the component's datasheet and is crucial for proper circuit design and operation.
100nA - Vce Saturation (Max) @ Ib, Ic
The parameter "Vce Saturation (Max) @ Ib, Ic" in electronic components refers to the maximum voltage drop across the collector-emitter junction when the transistor is in saturation mode. This parameter is specified at a certain base current (Ib) and collector current (Ic) levels. It indicates the minimum voltage required to keep the transistor fully conducting in saturation mode, ensuring that the transistor operates efficiently and does not enter the cutoff region. Designers use this parameter to ensure proper transistor operation and to prevent overheating or damage to the component.
650mV @ 5mA, 100mA - Voltage - Collector Emitter Breakdown (Max)
Voltage - Collector Emitter Breakdown (Max) is a parameter that specifies the maximum voltage that can be applied between the collector and emitter terminals of a transistor or other semiconductor device before it breaks down and allows excessive current to flow. This parameter is crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the component within its specified limits. Exceeding the maximum breakdown voltage can lead to permanent damage or failure of the device. Designers and engineers must carefully consider this parameter when selecting components for their circuits to prevent potential issues and ensure proper functionality.
45V - Frequency - Transition
The parameter "Frequency - Transition" in electronic components refers to the maximum frequency at which a signal transition can occur within the component. It is a crucial specification for digital circuits as it determines the speed at which data can be processed and transmitted. A higher frequency transition allows for faster operation and better performance of the electronic component. It is typically measured in hertz (Hz) or megahertz (MHz) and is specified by the manufacturer to ensure proper functioning of the component within a given frequency range.
320MHz - Collector Base Voltage (VCBO)
Collector Base Voltage (VCBO) is the maximum allowable voltage that can be applied between the collector and base terminals of a bipolar junction transistor when the emitter is open. It is a critical parameter that determines the voltage rating of the transistor and helps prevent breakdown in the collector-base junction. Exceeding this voltage can lead to permanent damage or failure of the component.
-50V - Emitter Base Voltage (VEBO)
Emitter Base Voltage (VEBO) is a parameter used in electronic components, particularly in transistors. It refers to the maximum voltage that can be applied between the emitter and base terminals of a transistor without causing damage to the device. Exceeding this voltage limit can lead to breakdown of the transistor and potential failure. VEBO is an important specification to consider when designing circuits to ensure the proper operation and reliability of the components. It is typically provided in the datasheet of the transistor and should be carefully observed to prevent any potential damage during operation.
5V - RoHS Status
RoHS means “Restriction of Certain Hazardous Substances” in the “Hazardous Substances Directive” in electrical and electronic equipment.
Non-RoHS Compliant - Lead Free
Lead Free is a term used to describe electronic components that do not contain lead as part of their composition. Lead is a toxic material that can have harmful effects on human health and the environment, so the electronics industry has been moving towards lead-free components to reduce these risks. Lead-free components are typically made using alternative materials such as silver, copper, and tin. Manufacturers must comply with regulations such as the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive to ensure that their products are lead-free and environmentally friendly.
Contains Lead
Datasheet PDF
- PCN Obsolescence/ EOL :
- ReachStatement :
- Datasheets :
 4N36 Optocoupler: Datasheet, Pinout, 4N35 vs.4N36 vs.4N37
4N36 Optocoupler: Datasheet, Pinout, 4N35 vs.4N36 vs.4N3725 October 20213440
 MIC2563A PCMCIA Switch: Pinout, Equivalent and Datasheet
MIC2563A PCMCIA Switch: Pinout, Equivalent and Datasheet08 March 2022583
 A Comprehensive Guide to the Analog Devices Inc. 5962-8773802GA Linear Amplifier
A Comprehensive Guide to the Analog Devices Inc. 5962-8773802GA Linear Amplifier06 March 202472
 SN74HC595N Shift Register: Datasheet, Pinout and Circuit
SN74HC595N Shift Register: Datasheet, Pinout and Circuit11 September 20216938
 A Comprehensive Guide to LTC6421IUDC-20#TRPBF ADC Driver
A Comprehensive Guide to LTC6421IUDC-20#TRPBF ADC Driver06 March 2024280
 MPX5010DP Transducer: Pinout, Specifications and Datasheet
MPX5010DP Transducer: Pinout, Specifications and Datasheet18 October 20216741
 AD8233ACBZ-R7 Heart Rate Monitor: Low Noise, 20WLCSP Monitor and AD8233 Datasheet
AD8233ACBZ-R7 Heart Rate Monitor: Low Noise, 20WLCSP Monitor and AD8233 Datasheet21 January 20221605
 ADM485 Transceiver : Datasheet, Pinout and Circuit
ADM485 Transceiver : Datasheet, Pinout and Circuit17 July 20213638
 Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor: Working Principles, Structure, and Types
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor: Working Principles, Structure, and Types31 March 202544226
 Analysis of SiP (System in Package)
Analysis of SiP (System in Package)12 January 20226005
 Dynamic On-Resistance and its Impact on Power Converters
Dynamic On-Resistance and its Impact on Power Converters28 August 20232344
 Humidity Sensor: Classification, Package and Application
Humidity Sensor: Classification, Package and Application13 November 20253851
 What is a Thermoelectric Cooler?
What is a Thermoelectric Cooler?08 April 20215973
 What are the Differences Between Pull up and Pull down Resistors?
What are the Differences Between Pull up and Pull down Resistors?22 October 202534212
 What is Time Delay Relay?
What is Time Delay Relay?18 December 202510951
 Designing a GaN-based Dual Active Bridge for PHEV Chargers
Designing a GaN-based Dual Active Bridge for PHEV Chargers17 May 20242286
ON Semiconductor
In Stock: 11940
United States
China
Canada
Japan
Russia
Germany
United Kingdom
Singapore
Italy
Hong Kong(China)
Taiwan(China)
France
Korea
Mexico
Netherlands
Malaysia
Austria
Spain
Switzerland
Poland
Thailand
Vietnam
India
United Arab Emirates
Afghanistan
Åland Islands
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antigua & Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba
Bosnia & Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
Christmas Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo
Congo (DRC)
Cook Islands
Costa Rica
Côte d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curaçao
Cyprus
Czechia
Denmark
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia
Georgia
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Honduras
Hungary
Iceland
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Jamaica
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macao(China)
Madagascar
Malawi
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Myanmar
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Korea
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Palestinian Authority
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Réunion
Romania
Rwanda
Samoa
San Marino
São Tomé & Príncipe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
South Sudan
Sri Lanka
St Helena, Ascension, Tristan da Cunha
St. Barthélemy
St. Kitts & Nevis
St. Lucia
St. Martin
St. Pierre & Miquelon
St. Vincent & Grenadines
Sudan
Suriname
Svalbard & Jan Mayen
Sweden
Syria
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad & Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks & Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
U.S. Outlying Islands
U.S. Virgin Islands
Uganda
Ukraine
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Vatican City
Venezuela
Wallis & Futuna
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe













