Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF price hacks every buyer should know
N-Channel Tape & Reel (TR) 45m Ω @ 4.2A, 4.5V ±12V 740pF @ 15V 12nC @ 5V TO-236-3, SC-59, SOT-23-3









N-Channel Tape & Reel (TR) 45m Ω @ 4.2A, 4.5V ±12V 740pF @ 15V 12nC @ 5V TO-236-3, SC-59, SOT-23-3
Secure the best price for Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF with sourcing tips, price comparison, bulk discounts, and ways to avoid hidden costs and counterfeits.
Product Introduction
If you want the best price on Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF, start with a price comparison tool. You can quickly spot the lowest pricing for this electronic part. Many buyers grab the first offer, but you should check every electronic source for better deals. Think about your current electronic sourcing habits. Have you ever missed a lower price on electronic components? You can save big on your next electronic purchasing move. Even if you buy electronic parts often, you might find a new electronic pricing trick here. The right electronic pricing strategy can turn your next electronic sourcing into a win.
Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF Sourcing
Distributors
When you start electronic sourcing for Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF, you want to look at trusted distributors first. These companies offer real electronic parts and clear pricing. You can find Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF at places like Mouser, DigiKey, Future Electronics, and Schukat. Each distributor updates electronic pricing often, so you should check their websites before purchasing. Here’s a quick look at where you can source this electronic part around the world:
| Region | Authorized Distributors |
|---|---|
| Americas | Arrow Electronics, Avnet, DigiKey, Future Electronics, Mouser Electronics, Newark, Rochester Electronics, RS Components |
| Asia Pacific | Arrow Electronics, Avnet, DigiKey, element14, Future Electronics, Mouser Electronics, Rochester Electronics, RS Components |
| China | Arrow Electronics, Avnet, DigiKey, element14, Future Electronics, Mouser Electronics, Rochester Electronics, RS Components, Rutronik |
| Europe, Middle East & Africa | Arrow Electronics, Avnet, DigiKey, EBV Elektronik, Farnell, Future Electronics, Mouser Electronics, Rochester Electronics, RS Components, Rutronik, TME |
| Japan | Arrow Electronics, Avnet, DigiKey, element14, Mouser Electronics, Rochester Electronics, RS Components |
You get reliable electronic sourcing, but sometimes the price is a bit higher than other channels. Still, you know you are getting genuine electronic parts.
Marketplaces
You might want to check electronic marketplaces for better pricing. Sites like eBay, Amazon, AliExpress, and Utsource.net list Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF from many sellers. You can see a wide range of electronic pricing here. Some sellers offer very low prices, but you need to watch out for authenticity. Here’s a chart that shows how electronic pricing can change between sellers:
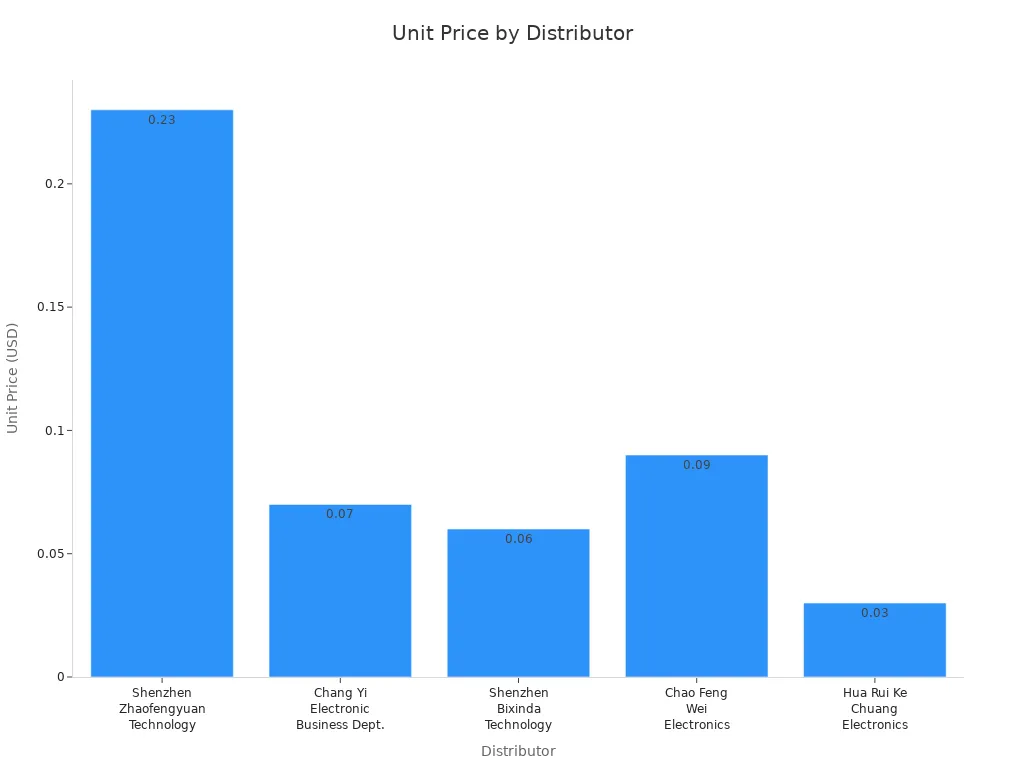
You may find electronic pricing as low as $0.03 per unit, but always check the seller’s reputation before purchasing. Sometimes, electronic sourcing from marketplaces means you wait longer for shipping or risk getting non-genuine electronic parts.
Stock and Availability
Electronic stock for Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF changes fast. Inventory levels go up and down every day. Distributors and marketplaces update electronic stock about every 24 hours. Before you finish your electronic purchasing, always confirm electronic stock with a salesperson or online chat. This step helps you avoid delays and missed orders. If you want the best electronic pricing, you need to act fast when you see good electronic stock and price. Quick action can help you win the electronic sourcing game.
Tip: Always double-check electronic stock and pricing before you buy. Fast-moving inventory can mean you miss out on the best electronic price if you wait too long.
Price Hacks
Bulk Buying
You can save a lot on electronic parts when you buy in bulk. Many suppliers lower the unit price if you order more. For example, if you buy just a few Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF, you might pay a higher price per piece. When you increase your order, the pricing drops. This is true for most electronic distributors and marketplaces.
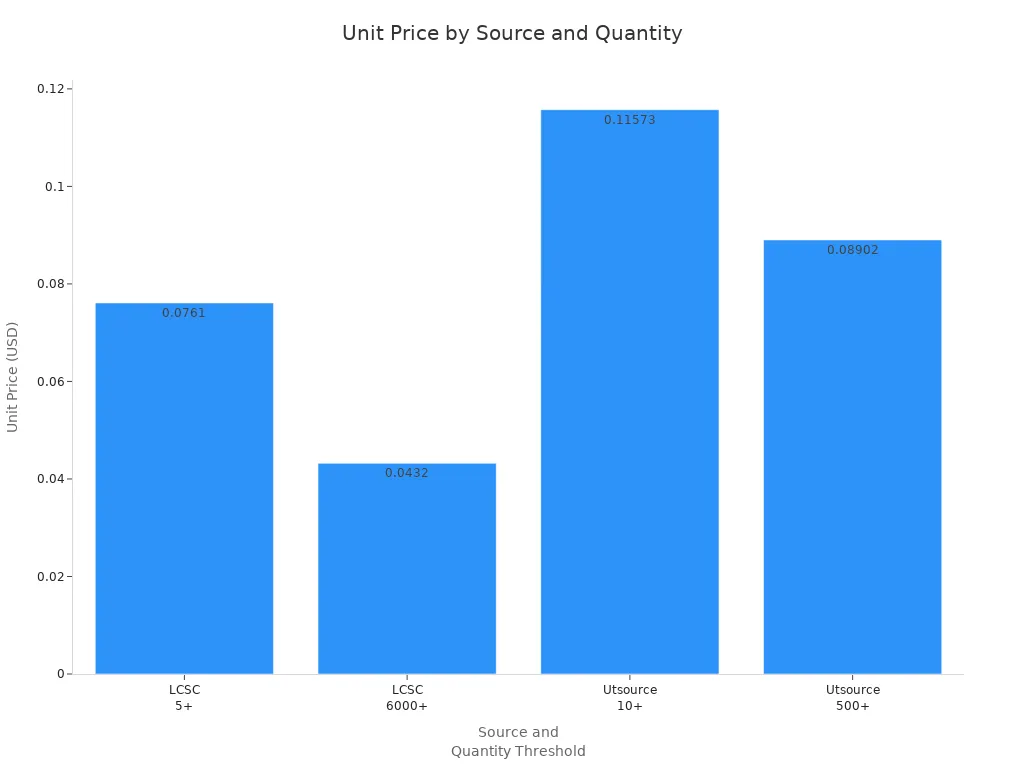
Let’s look at a real example. At LCSC, if you buy 5 or more, the unit price is $0.0761. If you buy 6,000 or more, the price drops to $0.0432 each. That is a big difference. Utsource also lowers the price for bigger orders. For 10 or more, the price is $0.11573 per unit. For 500 or more, the price drops to $0.08902. You can see how bulk buying helps you get better pricing on electronic parts.
| Source | Quantity Threshold | Unit Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| LCSC | 5+ | 0.0761 |
| LCSC | 6000+ | 0.0432 |
| Utsource | 10+ | 0.11573 |
| Utsource | 500+ | 0.08902 |
Tip: Always check the next price break before you buy. Sometimes, ordering just a few more electronic parts can save you money on the whole order.
Timing
Timing matters a lot in electronic sourcing. Prices and pricing change often. You can catch special deals during sales or promotions. Some distributors offer discounts at the end of the quarter or during big events. If you set up price alerts on comparison sites, you will know when the price drops. This helps you buy Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF at the best time.
You should also watch for stock updates. When electronic stock is high, pricing can go down. When stock is low, the price may go up. If you see a good deal, act fast. Waiting too long can mean missing out on the best pricing.
Note: Sign up for newsletters from your favorite electronic distributors. They often send out alerts about sales and special pricing.
Price Comparison
You should always compare prices before you buy electronic parts. Price comparison websites make this easy. They show you the pricing from many suppliers side by side. This helps you spot the best deal for Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF.
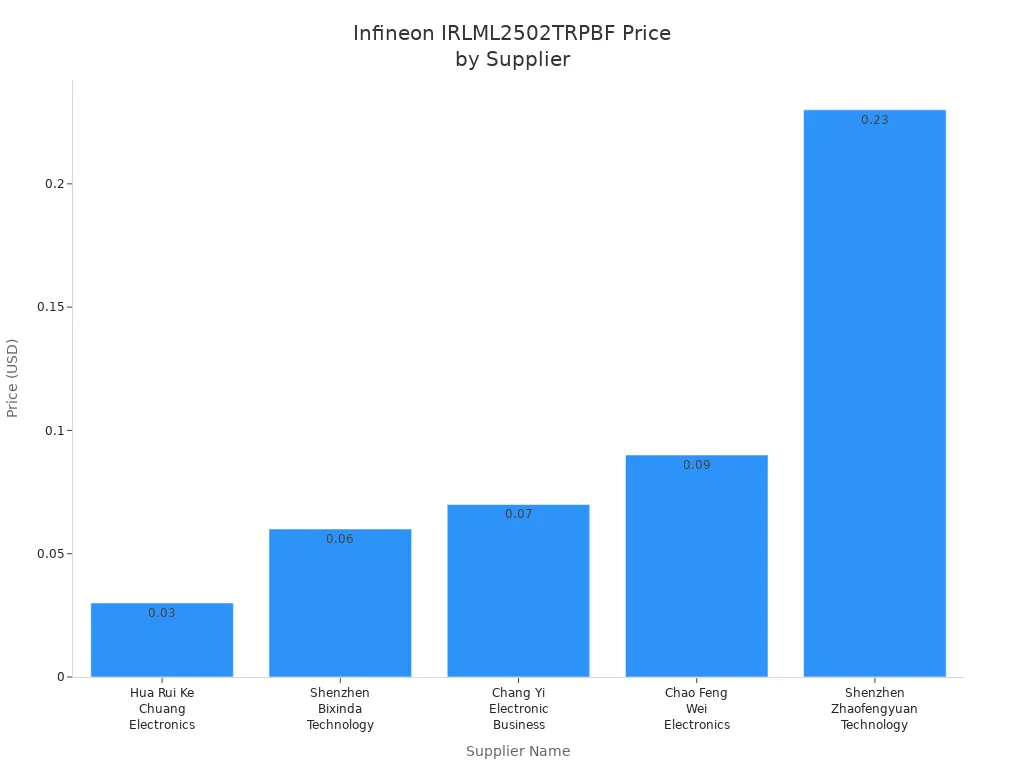
Here is how a price analysis of electronic import looks on a comparison site:
| Supplier Name | Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| Hua Rui Ke Chuang Electronics Co.,Ltd. | 0.03 |
| Shenzhen Bixinda Technology Co., Ltd. | 0.06 |
| Chang Yi Electronic Business Department | 0.07 |
| Chao Feng Wei Electronics Co.,Ltd. | 0.09 |
| Shenzhen Zhaofengyuan Technology Co., Ltd. | 0.23 |
You can see that the pricing can change a lot between sellers. Some offer a price as low as $0.03 per unit. Others charge much more. Always check shipping costs and delivery times, too. Sometimes a low price comes with high shipping fees.
You can also see big differences in pricing between platforms. For example, DigiKey lists Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF at $0.26 per unit. On eBay or Amazon, you might pay $8 to $10 for a pack of 10. That is $0.80 to $1.00 per unit. Always do a quick price analysis of electronic import before you buy.
Tip: Use at least two price comparison tools. This helps you catch the best pricing and avoid missing hidden deals on electronic parts.
Negotiation
You can often negotiate for a better price, especially if you buy a lot of electronic parts. Many distributors will give you a discount if you ask. You can also try to get free shipping or faster delivery. If you are a repeat customer, mention that. Sellers like to reward loyal buyers with better pricing.
Here are some negotiation tips:
Ask for a quote if you plan to buy a large quantity of Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF.
Request a discount on shipping fees, especially for bulk orders.
See if the seller can match a lower price you found elsewhere.
Ask about special pricing for students, schools, or businesses.
Pro Tip: Always be polite and clear about what you want. Sellers are more likely to help if you build a good relationship.
With these price hacks, you can get the best pricing on electronic parts every time. You will save money and avoid overpaying for Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF. Smart electronic sourcing starts with knowing how to work the system.
Avoiding Pitfalls
Counterfeits
You want to avoid fake electronic parts at all costs. Counterfeit Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF can sneak into the market, especially on some electronic marketplaces. If you buy from unknown sellers, you risk getting electronic parts that do not work or even damage your project. Always stick with authorized electronic distributors or verified sellers. They protect you from counterfeits and help you get the real deal. When you see a price that looks too good to be true, it probably is. Super low pricing on electronic parts can be a red flag. You do not want to save a little on price and lose a lot on quality.
Tip: Check seller ratings and reviews before you buy electronic parts. Trusted sellers care about their reputation and offer real electronic products.
Authenticity
You need to make sure your Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF is authentic. Real electronic parts come with clear labels, datasheets, and sometimes even traceable codes. Ask your electronic distributor for a certificate of authenticity if you are unsure. Some electronic suppliers offer tracking numbers or batch codes so you can check where your electronic part came from. If you buy from a marketplace, ask the seller for proof that the electronic part is genuine. Authentic electronic parts keep your project safe and reliable. Never skip this step, even if the price or pricing looks great.
Look for original packaging and manufacturer logos.
Request datasheets or certificates from your electronic supplier.
Use traceability codes to confirm the source of your electronic part.
Hidden Costs
The listed price for Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF often does not show the full story. You might see a low price or attractive pricing, but hidden costs can add up fast. Shipping fees, banking charges, and customs can push the total price much higher than you expect. For example, shipping can start at $2 and go up to $40 or more, depending on the method and where you live. Some banks charge $30 just to process your payment. Customs and handling fees may surprise you when your electronic order arrives.
Here’s a quick look at how these hidden costs affect your total price:
| Cost Component | Details and Range |
|---|---|
| Unit Price | Approximately $0.0761 per unit (small quantities) |
| Shipping Fees | Starting from $2 up to $40+ |
| Banking Fees | East West Bank charges $30; Western Union $0 |
| Customs/Handling | Possible extra charges by country |
| Delivery Time | 3-7 days (express); longer for registered mail |
You also need to remember that electronic stock and pricing change quickly. Sometimes, the price you see online does not match the real-time inventory. Always confirm your electronic order before you pay. Shipping with major carriers like DHL, FedEx, or UPS can be fast, but registered mail takes much longer. These factors can change your total price and delay your electronic project.
Note: Always add up all costs before you buy. The lowest price or best pricing on electronic parts might not be the cheapest after you count shipping and fees.
Extra Savings Tips
Loyalty Programs
You can unlock extra value by joining loyalty programs from top electronic distributors. These programs reward you for buying electronic parts like Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF, 3v lithium battery, and cr2032 battery. When you sign up, you get perks like coupons, free shipping, and even a 365-day warranty on your electronic purchases. Some programs offer a $5 shipping coupon for new users, a 30-day free PLUS trial that cuts the price of electronic parts by 10%, and a funds account for future electronic orders. You also get tiered pricing discounts, so the more electronic items you buy, the lower the price per unit. Here’s a quick look at what you can get:
| Loyalty Program Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| New User Coupon | $5 shipping coupon for new users |
| PLUS Service Trial | 30-day free PLUS trial reducing commodity prices by 10% |
| Funds Account | Returned money credited for future electronic purchases |
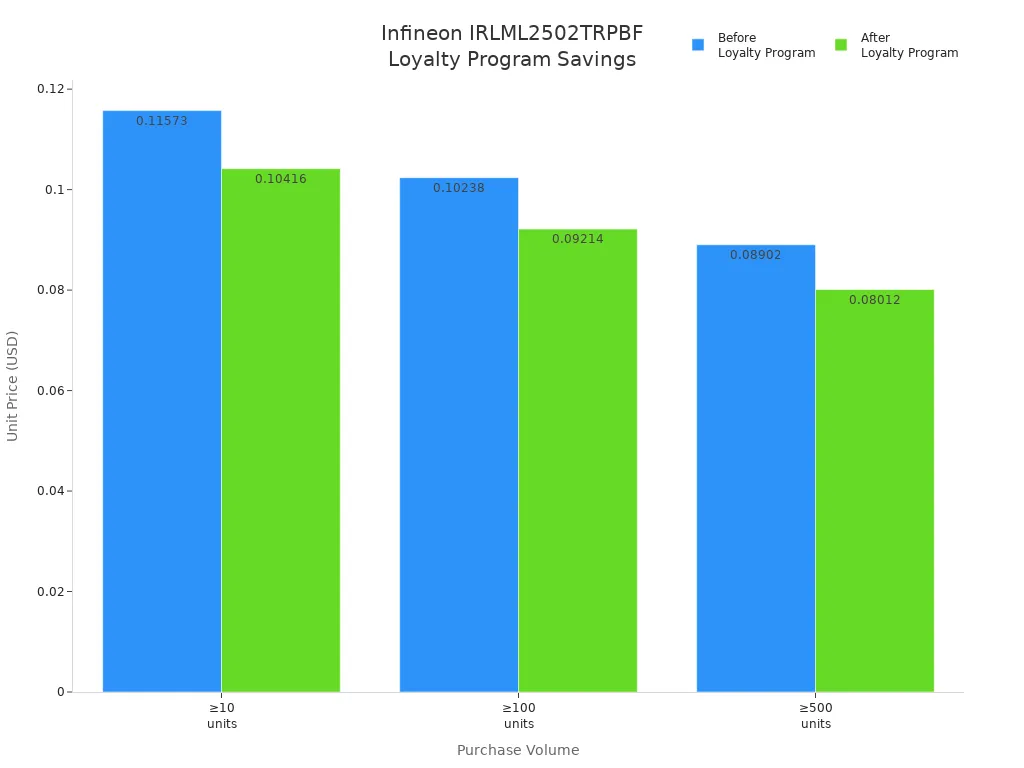
| Tiered Pricing Discounts | ≥10 units: $0.11573/unit; ≥100 units: $0.10238/unit; ≥500 units: $0.08902/unit |
| Free Shipping | Free shipping on orders over $300 (except US) |
| Warranty and Returns | 90 days money-back return; 100 days warranty against defects |
You can see real savings when you use these programs. For example, if you buy 100 electronic parts, the unit price drops from $0.10238 to $0.09214 with the PLUS trial. That’s more money in your pocket for your next electronic or battery project.
Tip: Always check for new user deals and free trials before you place your next electronic or battery order.
Free Samples
You can sometimes get free samples or evaluation units for electronic parts, including lithium and cr2032 battery options. Many electronic distributors want you to try their products, so they offer free samples for new projects or testing. If you need to test a 3v lithium battery or a new electronic component, ask your supplier about sample programs. This helps you save money and check the quality before you commit to a bigger electronic order. Free samples are perfect for students, hobbyists, or anyone starting a new electronic project.
Ask your electronic distributor for sample policies.
Use samples to test lithium or cr2032 battery performance.
Try before you buy to avoid wasting money on the wrong electronic part.
Group Buys
Group buys give you the power to lower the price of electronic parts like Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF, lithium, and cr2032 battery. When you join a group buy or collective purchasing forum, you combine your electronic order with others. This helps you reach higher quantity tiers and unlock better price breaks. For example, if your group orders 500 electronic units, the price drops to about $0.0801 per unit. Add a PLUS trial, and you save even more on your electronic and battery needs.
| Order Quantity Threshold | Approximate Unit Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| 10+ units | $0.1157 |
| 100+ units | $0.1024 |
| 500+ units | $0.0801 |
You can find group buys on electronic forums, social media, or through local maker clubs. This strategy works great for lithium, cr2032 battery, and other electronic components you use often.
Note: Group buys help you and your friends get the best price on electronic and battery orders. You also share shipping costs, which makes every electronic purchase even cheaper.
You now know how to get the best price on Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF. Use electronic price comparison tools, check electronic stock, and buy electronic parts in bulk. Always ask for a better price and watch for electronic deals. Join electronic loyalty programs and try to get electronic samples. Group buys can help you save on electronic and battery orders. Stay alert for electronic counterfeits and hidden electronic costs. Keep learning about electronic sourcing. Share your electronic and battery tips below. Your electronic price hacks can help others in the electronic and battery community. Ready to score the lowest price on your next electronic and battery order? Let’s make every electronic and battery purchase count!
FAQ
What is the best way to find the lowest electronic price for Infineon IRLML2502TRPBF?
You can use electronic price comparison tools. These tools show you prices from many electronic suppliers. You spot deals fast and avoid overpaying. Always check electronic stock before you buy.
How do you know if an electronic part is real or fake?
You should buy from trusted electronic distributors or sellers with good reviews. Ask for proof like datasheets or certificates. Real electronic parts come in original packaging. If you see a super low price, check the electronic source carefully.
Can you save money by buying more electronic parts at once?
Yes! When you buy electronic parts in bulk, the price per electronic unit drops. Many electronic suppliers offer discounts for bigger orders. Always check the next price break before you finish your electronic order.
Are there hidden costs when you buy electronic parts online?
Sometimes, yes. Shipping fees, taxes, and handling charges can raise the total electronic cost. Always add up all electronic costs before you pay. Ask the electronic seller for a full price list.
Where can you get extra savings on electronic parts?
You can join electronic loyalty programs, look for free electronic samples, or join group buys. These options help you save on every electronic order. Watch for electronic sales and special deals, too.
Specifications
- TypeParameter
- Factory Lead Time12 Weeks
- Contact Plating
Contact plating (finish) provides corrosion protection for base metals and optimizes the mechanical and electrical properties of the contact interfaces.
Tin - Mount
In electronic components, the term "Mount" typically refers to the method or process of physically attaching or fixing a component onto a circuit board or other electronic device. This can involve soldering, adhesive bonding, or other techniques to secure the component in place. The mounting process is crucial for ensuring proper electrical connections and mechanical stability within the electronic system. Different components may have specific mounting requirements based on their size, shape, and function, and manufacturers provide guidelines for proper mounting procedures to ensure optimal performance and reliability of the electronic device.
Surface Mount - Mounting Type
The "Mounting Type" in electronic components refers to the method used to attach or connect a component to a circuit board or other substrate, such as through-hole, surface-mount, or panel mount.
Surface Mount - Package / Case
refers to the protective housing that encases an electronic component, providing mechanical support, electrical connections, and thermal management.
TO-236-3, SC-59, SOT-23-3 - Number of Pins3
- Transistor Element Material
The "Transistor Element Material" parameter in electronic components refers to the material used to construct the transistor within the component. Transistors are semiconductor devices that amplify or switch electronic signals and are a fundamental building block in electronic circuits. The material used for the transistor element can significantly impact the performance and characteristics of the component. Common materials used for transistor elements include silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, each with its own unique properties and suitability for different applications. The choice of transistor element material is crucial in designing electronic components to meet specific performance requirements such as speed, power efficiency, and temperature tolerance.
SILICON - Current - Continuous Drain (Id) @ 25℃4.2A Ta
- Drive Voltage (Max Rds On, Min Rds On)2.5V 4.5V
- Number of Elements1
- Power Dissipation (Max)1.25W Ta
- Turn Off Delay Time
It is the time from when Vgs drops below 90% of the gate drive voltage to when the drain current drops below 90% of the load current. It is the delay before current starts to transition in the load, and depends on Rg. Ciss.
54 ns - Operating Temperature
The operating temperature is the range of ambient temperature within which a power supply, or any other electrical equipment, operate in. This ranges from a minimum operating temperature, to a peak or maximum operating temperature, outside which, the power supply may fail.
-55°C~150°C TJ - Packaging
Semiconductor package is a carrier / shell used to contain and cover one or more semiconductor components or integrated circuits. The material of the shell can be metal, plastic, glass or ceramic.
Tape & Reel (TR) - Series
In electronic components, the "Series" refers to a group of products that share similar characteristics, designs, or functionalities, often produced by the same manufacturer. These components within a series typically have common specifications but may vary in terms of voltage, power, or packaging to meet different application needs. The series name helps identify and differentiate between various product lines within a manufacturer's catalog.
HEXFET® - Published2004
- JESD-609 Code
The "JESD-609 Code" in electronic components refers to a standardized marking code that indicates the lead-free solder composition and finish of electronic components for compliance with environmental regulations.
e3 - Part Status
Parts can have many statuses as they progress through the configuration, analysis, review, and approval stages.
Active - Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL)
Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) is a standardized rating that indicates the susceptibility of electronic components, particularly semiconductors, to moisture-induced damage during storage and the soldering process, defining the allowable exposure time to ambient conditions before they require special handling or baking to prevent failures
1 (Unlimited) - Number of Terminations3
- Termination
Termination in electronic components refers to the practice of matching the impedance of a circuit to prevent signal reflections and ensure maximum power transfer. It involves the use of resistors or other components at the end of transmission lines or connections. Proper termination is crucial in high-frequency applications to maintain signal integrity and reduce noise.
SMD/SMT - ECCN Code
An ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) is an alphanumeric code used by the U.S. Bureau of Industry and Security to identify and categorize electronic components and other dual-use items that may require an export license based on their technical characteristics and potential for military use.
EAR99 - Resistance
Resistance is a fundamental property of electronic components that measures their opposition to the flow of electric current. It is denoted by the symbol "R" and is measured in ohms (Ω). Resistance is caused by the collisions of electrons with atoms in a material, which generates heat and reduces the flow of current. Components with higher resistance will impede the flow of current more than those with lower resistance. Resistance plays a crucial role in determining the behavior and functionality of electronic circuits, such as limiting current flow, voltage division, and controlling power dissipation.
45mOhm - Additional Feature
Any Feature, including a modified Existing Feature, that is not an Existing Feature.
HIGH RELIABILITY - Voltage - Rated DC
Voltage - Rated DC is a parameter that specifies the maximum direct current (DC) voltage that an electronic component can safely handle without being damaged. This rating is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning and longevity of the component in a circuit. Exceeding the rated DC voltage can lead to overheating, breakdown, or even permanent damage to the component. It is important to carefully consider this parameter when designing or selecting components for a circuit to prevent any potential issues related to voltage overload.
20V - Terminal Position
In electronic components, the term "Terminal Position" refers to the physical location of the connection points on the component where external electrical connections can be made. These connection points, known as terminals, are typically used to attach wires, leads, or other components to the main body of the electronic component. The terminal position is important for ensuring proper connectivity and functionality of the component within a circuit. It is often specified in technical datasheets or component specifications to help designers and engineers understand how to properly integrate the component into their circuit designs.
DUAL - Terminal Form
Occurring at or forming the end of a series, succession, or the like; closing; concluding.
GULL WING - Peak Reflow Temperature (Cel)
Peak Reflow Temperature (Cel) is a parameter that specifies the maximum temperature at which an electronic component can be exposed during the reflow soldering process. Reflow soldering is a common method used to attach electronic components to a circuit board. The Peak Reflow Temperature is crucial because it ensures that the component is not damaged or degraded during the soldering process. Exceeding the specified Peak Reflow Temperature can lead to issues such as component failure, reduced performance, or even permanent damage to the component. It is important for manufacturers and assemblers to adhere to the recommended Peak Reflow Temperature to ensure the reliability and functionality of the electronic components.
260 - Current Rating
Current rating is the maximum current that a fuse will carry for an indefinite period without too much deterioration of the fuse element.
4.2A - Time@Peak Reflow Temperature-Max (s)
Time@Peak Reflow Temperature-Max (s) refers to the maximum duration that an electronic component can be exposed to the peak reflow temperature during the soldering process, which is crucial for ensuring reliable solder joint formation without damaging the component.
30 - Element Configuration
The distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals.
Single - Operating Mode
A phase of operation during the operation and maintenance stages of the life cycle of a facility.
ENHANCEMENT MODE - Power Dissipation
the process by which an electronic or electrical device produces heat (energy loss or waste) as an undesirable derivative of its primary action.
1.25W - Turn On Delay Time
Turn-on delay, td(on), is the time taken to charge the input capacitance of the device before drain current conduction can start.
7.5 ns - FET Type
"FET Type" refers to the type of Field-Effect Transistor (FET) being used in an electronic component. FETs are three-terminal semiconductor devices that can be classified into different types based on their construction and operation. The main types of FETs include Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor FETs (MOSFETs), Junction FETs (JFETs), and Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs).Each type of FET has its own unique characteristics and applications. MOSFETs are commonly used in digital circuits due to their high input impedance and low power consumption. JFETs are often used in low-noise amplifiers and switching circuits. IGBTs combine the high input impedance of MOSFETs with the high current-carrying capability of bipolar transistors, making them suitable for high-power applications like motor control and power inverters.When selecting an electronic component, understanding the FET type is crucial as it determines the device's performance and suitability for a specific application. It is important to consider factors such as voltage ratings, current handling capabilities, switching speeds, and power dissipation when choosing the right FET type for a particular circuit design.
N-Channel - Transistor Application
In the context of electronic components, the parameter "Transistor Application" refers to the specific purpose or function for which a transistor is designed and used. Transistors are semiconductor devices that can amplify or switch electronic signals and are commonly used in various electronic circuits. The application of a transistor can vary widely depending on its design and characteristics, such as whether it is intended for audio amplification, digital logic, power control, or radio frequency applications. Understanding the transistor application is important for selecting the right type of transistor for a particular circuit or system to ensure optimal performance and functionality.
SWITCHING - Rds On (Max) @ Id, Vgs
Rds On (Max) @ Id, Vgs refers to the maximum on-resistance of a MOSFET or similar transistor when it is fully turned on or in the saturation region. It is specified at a given drain current (Id) and gate-source voltage (Vgs). This parameter indicates how much resistance the component will offer when conducting, impacting power loss and efficiency in a circuit. Lower Rds On values are preferred for better performance in switching applications.
45m Ω @ 4.2A, 4.5V - Vgs(th) (Max) @ Id
The parameter "Vgs(th) (Max) @ Id" in electronic components refers to the maximum gate-source threshold voltage at a specified drain current (Id). This parameter is commonly found in field-effect transistors (FETs) and is used to define the minimum voltage required at the gate terminal to turn on the transistor and allow current to flow from the drain to the source. The maximum value indicates the upper limit of this threshold voltage under specified operating conditions. It is an important parameter for determining the proper biasing and operating conditions of the FET in a circuit to ensure proper functionality and performance.
1.2V @ 250μA - Input Capacitance (Ciss) (Max) @ Vds
The parameter "Input Capacitance (Ciss) (Max) @ Vds" in electronic components refers to the maximum input capacitance measured at a specific drain-source voltage (Vds). Input capacitance is a crucial parameter in field-effect transistors (FETs) and power MOSFETs, as it represents the total capacitance at the input terminal of the device. This capacitance affects the device's switching speed and overall performance, as it influences the time required for charging and discharging during operation. Manufacturers provide this parameter to help designers understand the device's input characteristics and make informed decisions when integrating it into a circuit.
740pF @ 15V - Gate Charge (Qg) (Max) @ Vgs
Gate Charge (Qg) (Max) @ Vgs refers to the maximum amount of charge that must be supplied to the gate of a MOSFET or similar device to fully turn it on, measured at a specific gate-source voltage (Vgs). This parameter is crucial for understanding the switching characteristics of the device, as it influences the speed at which the gate can charge and discharge. A higher gate charge value often implies slower switching speeds, which can impact the efficiency of high-frequency applications. This parameter is typically specified in nanocoulombs (nC) in the component's datasheet.
12nC @ 5V - Rise Time
In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time is the time taken by a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value.
10ns - Vgs (Max)
Vgs (Max) refers to the maximum gate-source voltage that can be applied to a field-effect transistor (FET) without causing damage to the component. This parameter is crucial in determining the safe operating limits of the FET and helps prevent overvoltage conditions that could lead to device failure. Exceeding the specified Vgs (Max) rating can result in breakdown of the gate oxide layer, leading to permanent damage to the FET. Designers must ensure that the applied gate-source voltage does not exceed the maximum rating to ensure reliable and long-term operation of the electronic component.
±12V - Fall Time (Typ)
Fall Time (Typ) is a parameter used to describe the time it takes for a signal to transition from a high level to a low level in an electronic component, such as a transistor or an integrated circuit. It is typically measured in nanoseconds or microseconds and is an important characteristic that affects the performance of the component in digital circuits. A shorter fall time indicates faster switching speeds and can result in improved overall circuit performance, such as reduced power consumption and increased data transmission rates. Designers often consider the fall time specification when selecting components for their circuits to ensure proper functionality and efficiency.
26 ns - Continuous Drain Current (ID)
Continuous Drain Current (ID) is a key parameter in electronic components, particularly in field-effect transistors (FETs) such as MOSFETs. It refers to the maximum current that can flow continuously through the drain terminal of the FET without causing damage to the component. This parameter is crucial for determining the power handling capability of the FET and is specified by the manufacturer in the component's datasheet. Designers must ensure that the actual operating current does not exceed the specified Continuous Drain Current to prevent overheating and potential failure of the component.
4.2A - Threshold Voltage
The threshold voltage is a critical parameter in electronic components, particularly in field-effect transistors (FETs). It refers to the minimum voltage required at the input terminal of the FET to turn it on and allow current to flow between the source and drain terminals. Below the threshold voltage, the FET remains in the off state, acting as an open switch. Once the threshold voltage is exceeded, the FET enters the on state, conducting current between the source and drain.The threshold voltage is a key factor in determining the operating characteristics of FETs, such as their switching speed and power consumption. It is typically specified by the manufacturer and can vary depending on the specific type of FET and its design. Designers must consider the threshold voltage when selecting FETs for a particular application to ensure proper functionality and performance.
1.2V - Gate to Source Voltage (Vgs)
The Gate to Source Voltage (Vgs) is a crucial parameter in electronic components, particularly in field-effect transistors (FETs) such as MOSFETs. It refers to the voltage difference between the gate and source terminals of the FET. This voltage determines the conductivity of the FET and controls the flow of current through the device. By varying the Vgs, the FET can be switched on or off, allowing for precise control of electronic circuits. Understanding and properly managing the Vgs is essential for ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of FET-based circuits.
12V - Drain to Source Breakdown Voltage
Drain to Source Breakdown Voltage, often denoted as V(BR) D-S, is a critical parameter in electronic components, particularly in field-effect transistors (FETs) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FETs (MOSFETs). It represents the maximum voltage that can be applied between the drain and source terminals of the device without causing breakdown or permanent damage. Exceeding this voltage can lead to excessive current flow, resulting in thermal failure or destruction of the component. It is essential for ensuring reliable operation in circuit designs where high voltages may be encountered.
20V - Dual Supply Voltage
Dual Supply Voltage refers to an electronic component's requirement for two separate power supply voltages, typically one positive and one negative. This configuration is commonly used in operational amplifiers, analog circuits, and certain digital devices to allow for greater signal handling capabilities and improved performance. The use of dual supply voltages enables the device to process bipolar signals, thereby enhancing its functionality in various applications.
20V - Nominal Vgs
Nominal Vgs refers to the standard or expected gate-source voltage in field-effect transistors (FETs) and other related electronic components. It represents the voltage level at which the transistor operates optimally, ensuring proper switching characteristics and performance. This parameter is crucial for designers to determine the appropriate control signals required for efficient operation of the device in circuits. Variations from the nominal Vgs can affect the performance and reliability of the component.
1.2 V - Height1.016mm
- Length2.794mm
- Width3.05mm
- REACH SVHC
The parameter "REACH SVHC" in electronic components refers to the compliance with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation regarding Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC). SVHCs are substances that may have serious effects on human health or the environment, and their use is regulated under REACH to ensure their safe handling and minimize their impact.Manufacturers of electronic components need to declare if their products contain any SVHCs above a certain threshold concentration and provide information on the safe use of these substances. This information allows customers to make informed decisions about the potential risks associated with using the components and take appropriate measures to mitigate any hazards.Ensuring compliance with REACH SVHC requirements is essential for electronics manufacturers to meet regulatory standards, protect human health and the environment, and maintain transparency in their supply chain. It also demonstrates a commitment to sustainability and responsible manufacturing practices in the electronics industry.
No SVHC - Radiation Hardening
Radiation hardening is the process of making electronic components and circuits resistant to damage or malfunction caused by high levels of ionizing radiation, especially for environments in outer space (especially beyond the low Earth orbit), around nuclear reactors and particle accelerators, or during nuclear accidents or nuclear warfare.
No - RoHS Status
RoHS means “Restriction of Certain Hazardous Substances” in the “Hazardous Substances Directive” in electrical and electronic equipment.
ROHS3 Compliant - Lead Free
Lead Free is a term used to describe electronic components that do not contain lead as part of their composition. Lead is a toxic material that can have harmful effects on human health and the environment, so the electronics industry has been moving towards lead-free components to reduce these risks. Lead-free components are typically made using alternative materials such as silver, copper, and tin. Manufacturers must comply with regulations such as the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive to ensure that their products are lead-free and environmentally friendly.
Lead Free
Parts with Similar Specs
- ImagePart NumberManufacturerMountPackage / CaseContinuous Drain Current (ID)Current - Continuous Drain (Id) @ 25°CThreshold VoltageGate to Source Voltage (Vgs)Power DissipationPower Dissipation-MaxView Compare
IRLML2502TRPBF
Surface Mount
TO-236-3, SC-59, SOT-23-3
4.2 A
4.2A (Ta)
1.2 V
12 V
1.25 W
1.25W (Ta)
Surface Mount
TO-236-3, SC-59, SOT-23-3
4.6 A
4.6A (Ta)
-
12 V
1.25 W
1.25W (Ta)
Surface Mount
TO-236-3, SC-59, SOT-23-3
3 A
3A (Ta)
850 mV
8 V
500 mW
500mW (Ta)
Surface Mount
TO-236-3, SC-59, SOT-23-3
4.3 A
4.3A (Ta)
-1.1 V
12 V
1.3 W
1.3W (Ta)
Surface Mount
TO-236-3, SC-59, SOT-23-3
-3.7 A
3.7A (Ta)
-550 mV
12 V
1.3 W
1.3W (Ta)
Datasheet PDF
- PCN Packaging :
- Datasheets :
- Other Related Documents :
- PCN Assembly/Origin :
- ConflictMineralStatement :
 PIC16F688 Microcontroller: Circuit, Pinout, and Datasheet
PIC16F688 Microcontroller: Circuit, Pinout, and Datasheet11 November 20214808
 A Comprehensive Guide to LTC6601IUF-2#PBF Active Filter Interface
A Comprehensive Guide to LTC6601IUF-2#PBF Active Filter Interface06 March 202469
 LF353N Dual JFET Input Op-Amp: Datasheet, Pinout and Equivalents
LF353N Dual JFET Input Op-Amp: Datasheet, Pinout and Equivalents15 September 202111391
 TL064 Operational Amplifier: Features, Pinout and Datasheet
TL064 Operational Amplifier: Features, Pinout and Datasheet16 July 20213700
 A Comprehensive Guide to LTC7138MPMSE#TRPBF DC-DC Switching Regulator
A Comprehensive Guide to LTC7138MPMSE#TRPBF DC-DC Switching Regulator06 March 2024200
 1N5820 Rectifier: Datasheet, Features and Applications
1N5820 Rectifier: Datasheet, Features and Applications28 August 2021902
 M95040-W Serial SPI bus EEPROM: Pinout, Equivalent and Datasheet
M95040-W Serial SPI bus EEPROM: Pinout, Equivalent and Datasheet14 January 20224849
 TL1431 Adjustable Voltage Reference: Pinout, Specification and Datasheet
TL1431 Adjustable Voltage Reference: Pinout, Specification and Datasheet19 November 20211412
 Diodes Tutorial: How to Test Diodes?
Diodes Tutorial: How to Test Diodes?22 October 20259612
 What is a Synchronous Motor?
What is a Synchronous Motor?16 March 20215056
 Domestic SSD Master Chip Maker, Achieving a New Breakthrough in PCIe 5.0
Domestic SSD Master Chip Maker, Achieving a New Breakthrough in PCIe 5.027 April 2022632
 Challenges and Issues in Smart Grid Infrastructure
Challenges and Issues in Smart Grid Infrastructure11 May 20234043
 Always charge the battery to 100%? Stop it!
Always charge the battery to 100%? Stop it!15 October 20213752
 Near Field Communication (NFC) Explained: Working and Applications
Near Field Communication (NFC) Explained: Working and Applications24 May 202111883
 Microwave Diode: Introduction and Types
Microwave Diode: Introduction and Types07 January 202122590
 Getting Started with Raspberry Pi: A Beginner's Guide
Getting Started with Raspberry Pi: A Beginner's Guide23 August 20233080
Infineon Technologies
In Stock: 5880
United States
China
Canada
Japan
Russia
Germany
United Kingdom
Singapore
Italy
Hong Kong(China)
Taiwan(China)
France
Korea
Mexico
Netherlands
Malaysia
Austria
Spain
Switzerland
Poland
Thailand
Vietnam
India
United Arab Emirates
Afghanistan
Åland Islands
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antigua & Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba
Bosnia & Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
Christmas Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo
Congo (DRC)
Cook Islands
Costa Rica
Côte d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curaçao
Cyprus
Czechia
Denmark
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia
Georgia
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Honduras
Hungary
Iceland
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Jamaica
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macao(China)
Madagascar
Malawi
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Myanmar
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Korea
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Palestinian Authority
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Réunion
Romania
Rwanda
Samoa
San Marino
São Tomé & Príncipe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
South Sudan
Sri Lanka
St Helena, Ascension, Tristan da Cunha
St. Barthélemy
St. Kitts & Nevis
St. Lucia
St. Martin
St. Pierre & Miquelon
St. Vincent & Grenadines
Sudan
Suriname
Svalbard & Jan Mayen
Sweden
Syria
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad & Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks & Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
U.S. Outlying Islands
U.S. Virgin Islands
Uganda
Ukraine
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Vatican City
Venezuela
Wallis & Futuna
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe









