STMicroelectronics STM32L476QGI6: Microcontroller for Energy-Efficient IoT and Wearable Applications
1MB 1M x 8 FLASH ARM® Cortex®-M4 32-Bit Microcontroller STM32L4 Series STM32L476 132 Pin 80MHz 3V 132-UFBGA









1MB 1M x 8 FLASH ARM® Cortex®-M4 32-Bit Microcontroller STM32L4 Series STM32L476 132 Pin 80MHz 3V 132-UFBGA
The STM32L476QGI6 microcontroller offers ultra-low power modes, ARM Cortex-M4 efficiency, and flexible power management, ideal for energy-sensitive applications.
Product Introduction
The STM32L476QGI6 microcontroller offers groundbreaking energy efficiency for modern devices. Its ultra-low power modes set it apart, enabling operations with minimal energy draw. For example, it consumes just 300 nA in VBAT mode, supporting RTC and backup registers. In Standby mode, it uses only 120 nA, while Stop 2 mode operates at 1.1 µA. These features prolong battery life and reduce energy costs, making this microcontroller ideal for portable and energy-sensitive applications. Whether you're designing wearable technology or IoT devices, the STM32L476QGI6 ensures your product stays powered longer without sacrificing performance.
Understanding Low-Power Applications
Defining Low-Power Applications
Low-power applications refer to technologies and devices designed to operate with minimal energy consumption. These applications prioritize efficiency, ensuring that systems perform their tasks while consuming as little power as possible. You often encounter them in devices like smartwatches, IoT sensors, and portable medical equipment. Their primary goal is to extend battery life and reduce energy costs without compromising functionality.
The market for low-power applications is growing rapidly. It is expected to reach $7.5 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.6%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and IoT devices. Here's a quick overview of the market:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size | Expected to reach $7.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 9.6%. |
| Key Features | Integrated power monitoring, low power consumption, and scalability for large-scale deployment. |
| Applications | Consumer electronics, automotive systems, and IoT devices for improved battery life. |
Importance of Low-Power Applications in Modern Technology
Low-power applications play a crucial role in shaping modern technology. They enable the development of innovative solutions that address energy constraints in various industries. For example, IoT devices rely on low-power designs to function efficiently in remote locations. These devices often monitor environmental conditions, track assets, or manage resources like water and gas.
The adoption of low-power technologies also supports sustainability efforts. By reducing energy consumption, you contribute to lower carbon emissions and a greener planet. Additionally, industries such as agriculture, healthcare, and transportation benefit from these applications. Smart sensors in agriculture monitor soil health, while wearable devices in healthcare track vital signs. These advancements improve efficiency and enhance quality of life.
The STM32L476QGI6 microcontroller exemplifies the potential of low-power applications. Its ultra-low power modes and advanced features make it an ideal choice for energy-sensitive environments. Whether you're designing IoT devices or wearable technology, this microcontroller ensures optimal performance with minimal energy usage.
Key Features of STM32L476QGI6
ARM Cortex-M4 Core for High Performance and Low Power
The STM32L476QGI6 microcontroller features the ARM Cortex-M4 core, which strikes a perfect balance between performance and energy efficiency. You benefit from its ability to process tasks faster while consuming less power.
The Cortex-M4 achieves approximately 50% better performance per clock tick compared to the Cortex-M0, making it ideal for demanding applications.
The STM32F4 microcontroller, which uses the same core, delivers a benchmark rating of 225 Dhrystone MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second).
With a maximum clock frequency of 80 MHz, the STM32L476QGI6 ensures smooth operation for complex tasks while maintaining low power consumption.
This combination of speed and efficiency makes the STM32L476QGI6 a reliable choice for applications requiring high computational power without draining energy reserves.
Ultra-Low Power Modes for Energy Efficiency
The STM32L476QGI6 excels in energy efficiency, thanks to its ultra-low power modes. These modes allow you to optimize energy usage based on your application's requirements.
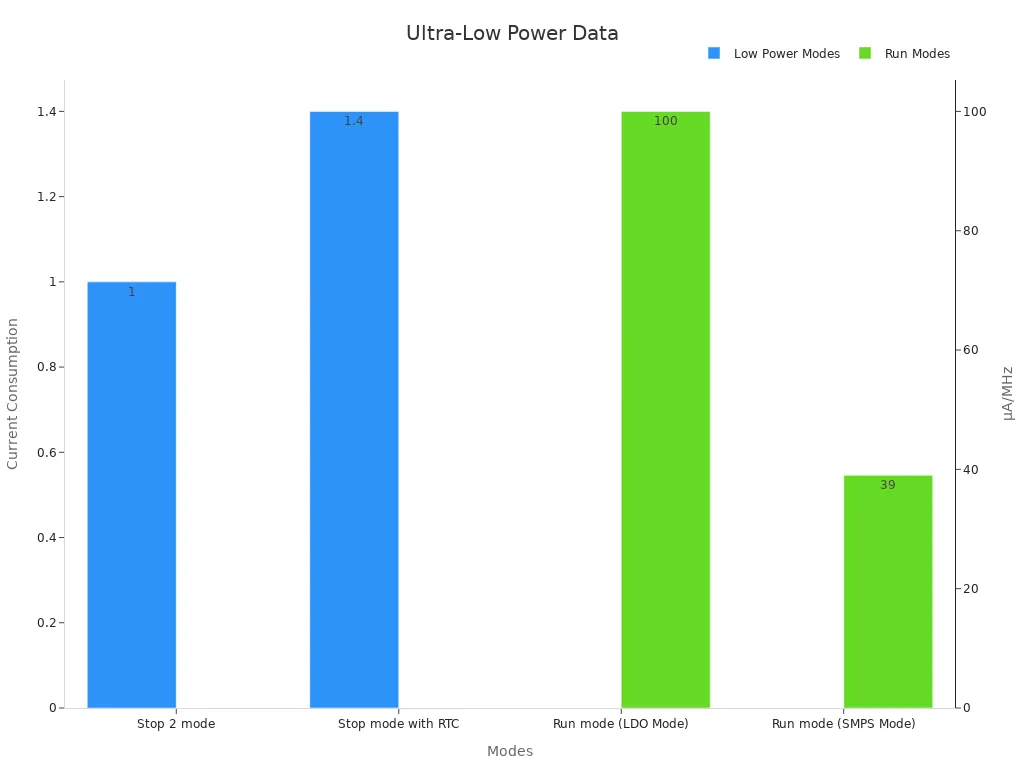
The ULPBench methodology confirms the effectiveness of these modes, providing systematic benchmarks for energy consumption. For example, in Stop 2 mode, the microcontroller consumes just 1 µA, while Stop mode with RTC uses 1.4 µA. Run mode offers two configurations: LDO Mode at 100 µA/MHz and SMPS Mode at 39 µA/MHz.
| Mode | Current Consumption |
|---|---|
| Stop 2 mode | 1 µA |
| Stop mode with RTC | 1.4 µA |
| Run mode (LDO Mode) | 100 µA/MHz |
| Run mode (SMPS Mode) | 39 µA/MHz |
| Wakeup from Stop mode | 4 µs |
These modes ensure your device operates efficiently, whether it's in active use or idle. The STM32L476QGI6 also boasts impressive energy benchmark scores, including a ULPMark™ CP score of 294 and a ULPMark™ PP score of 106.
Smart Analog and Digital Features
The STM32L476QGI6 integrates advanced analog and digital features to enhance functionality. You can leverage its 19 channels of 12-bit ADC for precise signal measurement and its 2 channels of 12-bit DAC for accurate signal generation.
Its connectivity options include CANbus, I2C, SPI, UART, and USB OTG, ensuring seamless communication across devices. Integrated peripherals like DMA, LCD controllers, PWM, and Watchdog Timers simplify complex designs.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| ADC Channels | 19 channels of 12-bit ADC |
| DAC Channels | 2 channels of 12-bit DAC |
| Connectivity Options | CANbus, I2C, SPI, UART, USB OTG |
| Integrated Peripherals | DMA, LCD controller, PWM, Watchdog Timer |
These features make the STM32L476QGI6 versatile for applications ranging from industrial automation to wearable technology. Its operating voltage range of 1.71V to 3.6V and temperature range of -40°C to 85°C further enhance its adaptability.
Flexible Power Management Architecture
The STM32L476QGI6 microcontroller stands out with its flexible power management architecture. This feature allows you to tailor energy usage to meet specific application needs. Whether you're designing a device for continuous operation or one that spends most of its time in idle mode, this microcontroller adapts to your requirements seamlessly.
Key Components of the Power Management Architecture
Dynamic Voltage Scaling (DVS):
You can adjust the operating voltage dynamically based on the workload. Lowering the voltage during less demanding tasks reduces power consumption significantly.Multiple Power Domains:
The STM32L476QGI6 divides its internal circuitry into separate power domains. This segmentation lets you deactivate unused sections of the microcontroller, saving energy during idle periods.Low-Power Clock Management:
The microcontroller includes advanced clock management features. You can reduce clock speeds or disable clocks for inactive peripherals, ensuring efficient energy use.Battery Backup Support:
The VBAT pin enables the microcontroller to operate in backup mode using minimal power. This feature is ideal for applications requiring long-term data retention, such as real-time clocks or memory storage.
Benefits of Flexible Power Management
Tip: Leveraging the STM32L476QGI6's power management architecture can extend battery life and improve device reliability.
Optimized Energy Usage:
By activating only the necessary components, you minimize energy waste. This optimization is crucial for portable devices like wearables and IoT sensors.Enhanced Performance:
The architecture ensures that performance remains consistent even when operating in low-power modes. You can achieve high computational efficiency without compromising energy savings.Adaptability Across Applications:
Whether you're developing industrial automation systems or smart home devices, the STM32L476QGI6's power management features adapt to diverse use cases.
Practical Example
Imagine you're designing a smart sensor for environmental monitoring. The sensor spends most of its time in sleep mode, waking periodically to collect data. With the STM32L476QGI6, you can use its Stop 2 mode to reduce power consumption to just 1 µA during sleep. When the sensor wakes, the microcontroller quickly transitions to Run mode, ensuring smooth data processing. This flexibility makes the STM32L476QGI6 an excellent choice for energy-sensitive applications.
Benefits of STM32L476QGI6 for Low-Power Applications
Prolonged Battery Life for Portable Devices
When designing portable devices, battery life is often your top priority. The STM32L476QGI6 microcontroller helps you achieve this goal with its ultra-low power consumption. Its advanced power-saving modes, such as Stop 2 mode, allow your device to consume as little as 1 µA during idle periods. This means your device can stay operational for extended periods without frequent recharging.
For example, if you're developing a fitness tracker, the microcontroller's ability to operate efficiently in low-power modes ensures the tracker can monitor activity continuously without draining the battery. Additionally, its dynamic voltage scaling feature adjusts power usage based on workload, further extending battery life.
Tip: By leveraging the STM32L476QGI6's power management features, you can create devices that last longer on a single charge, enhancing user satisfaction and reducing maintenance needs.
Cost Savings in Energy-Constrained Systems
Energy efficiency directly translates to cost savings, especially in systems where power availability is limited. The STM32L476QGI6 microcontroller minimizes energy waste, reducing the need for frequent battery replacements or expensive power sources.
For instance, in remote IoT applications like environmental monitoring, replacing batteries can be costly and time-consuming. The STM32L476QGI6's ability to operate at just 39 µA/MHz in SMPS mode ensures your system consumes minimal energy, lowering operational costs. Its VBAT mode, which uses only 300 nA, supports essential functions like real-time clocks while conserving power.
By choosing this microcontroller, you not only save on energy expenses but also contribute to sustainability by reducing electronic waste. This makes it an excellent choice for energy-constrained systems in industries like agriculture, healthcare, and smart cities.
Enhanced Performance in Energy-Sensitive Environments
The STM32L476QGI6 excels in energy-sensitive environments where both performance and efficiency are critical. Its ARM Cortex-M4 core delivers high computational power while maintaining low energy consumption. This balance ensures your device performs complex tasks without compromising battery life.
The microcontroller's robust peripheral set and advanced power-saving modes enhance its versatility. Whether you're developing industrial automation systems or wearable devices, it adapts to your application's needs. Here's a breakdown of its key features:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Low Power Consumption | Designed for energy-sensitive applications. |
| Advanced Power-Saving Modes | Enhances energy efficiency in various scenarios. |
| High System Integration | Supports a wide range of applications. |
| Robust Peripheral Set | Enables diverse communication protocols. |
| Low Power Operation | Ideal for battery-driven devices. |
Imagine you're building a smart home device that requires constant connectivity. The STM32L476QGI6's low-power operation ensures the device remains responsive while consuming minimal energy. Its ability to wake up from Stop mode in just 4 µs guarantees seamless performance, even in demanding scenarios.
Note: The STM32L476QGI6's combination of energy efficiency and high performance makes it a standout choice for applications where power and functionality must go hand in hand.
Comparing STM32L476QGI6 to Alternatives
Advantages Over Other STM32 Microcontrollers
The STM32L476QGI6 stands out among other STM32 microcontrollers due to its exceptional energy efficiency and advanced features. While many STM32 devices offer low-power modes, this microcontroller takes it a step further with its ultra-low power consumption. For instance, its Stop 2 mode consumes just 1 µA, which is significantly lower than what most STM32 microcontrollers achieve.
Another advantage lies in its ARM Cortex-M4 core. Unlike the Cortex-M0 or M3 cores found in other STM32 models, the M4 core delivers higher computational power while maintaining energy efficiency. This makes it ideal for applications requiring both performance and low power, such as wearable devices or IoT sensors.
The STM32L476QGI6 also offers a broader range of integrated peripherals. Its 19 ADC channels and 2 DAC channels provide greater flexibility for analog signal processing compared to other STM32 microcontrollers. Additionally, its support for multiple communication protocols, including CANbus and USB OTG, ensures seamless connectivity in diverse applications.
Comparison with Competitor Microcontrollers
When compared to competitor microcontrollers, the STM32L476QGI6 excels in energy efficiency and versatility. Many microcontrollers from competitors, such as Microchip’s PIC32 series or NXP’s LPC series, lack the same level of power-saving modes. For example, the STM32L476QGI6 consumes only 39 µA/MHz in SMPS mode, which is significantly lower than the typical consumption of competitor devices.
Its advanced power management architecture also sets it apart. Features like dynamic voltage scaling and multiple power domains allow you to optimize energy usage more effectively than with most competitor microcontrollers. These capabilities make it a preferred choice for energy-sensitive applications.
In addition, the STM32L476QGI6 offers a more comprehensive set of peripherals. While competitor microcontrollers may provide basic ADC and DAC functionality, the STM32L476QGI6’s 12-bit ADC and DAC channels deliver higher precision. Its ability to wake up from Stop mode in just 4 µs further enhances its performance in time-critical applications.
If you’re looking for a microcontroller that combines energy efficiency, performance, and versatility, the STM32L476QGI6 outshines both its STM32 siblings and competitor devices.
Practical Use Cases for STM32L476QGI6
IoT Devices and Smart Sensors
The STM32L476QGI6 microcontroller is perfect for IoT devices and smart sensors. These devices often operate in remote locations where energy efficiency is critical. You can use this microcontroller to power sensors that monitor temperature, humidity, or air quality. Its ultra-low power modes allow these sensors to run for years on a single battery.
For example, imagine a smart home system with multiple sensors. Each sensor collects data and communicates with a central hub. The STM32L476QGI6 ensures the sensors consume minimal energy while staying responsive. Its advanced connectivity options, like I2C and SPI, make it easy to integrate with other devices.
Tip: Use the STM32L476QGI6 to create IoT solutions that are both reliable and energy-efficient.
Wearable Technology
Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, demand compact and efficient components. The STM32L476QGI6 meets these needs with its small size and low power consumption. You can design wearables that track activity, monitor health, or provide notifications without frequent recharging.
The microcontroller’s ARM Cortex-M4 core delivers high performance for processing complex tasks. For instance, a fitness tracker can analyze heart rate data in real-time while conserving battery life. Its flexible power management ensures the device operates efficiently, even during intensive use.
Note: The STM32L476QGI6 helps you build wearables that combine functionality with long battery life.
Industrial Automation and Energy Harvesting
Industrial systems often require robust and energy-efficient solutions. The STM32L476QGI6 excels in these environments. You can use it to control machines, monitor processes, or manage energy resources. Its ability to operate in ultra-low power modes makes it ideal for energy-harvesting applications.
For example, a factory might use sensors powered by harvested energy to monitor equipment. The STM32L476QGI6 ensures these sensors function reliably with minimal power. Its wide operating temperature range and advanced peripherals make it suitable for harsh industrial conditions.
Tip: Leverage the STM32L476QGI6 for industrial systems that need durability and energy efficiency.
The STM32L476QGI6 microcontroller delivers unmatched energy efficiency and versatility for low-power applications. Its ultra-low power modes, ARM Cortex-M4 core, and flexible power management architecture make it ideal for devices that require long battery life and reliable performance. You can use it to create solutions for industries like IoT, wearables, and industrial automation.
Note: Choosing the STM32L476QGI6 ensures your designs meet modern energy demands while maintaining high functionality.
Explore this microcontroller for your next project to unlock its full potential and achieve low-power success.
FAQ
1. What makes the STM32L476QGI6 ideal for low-power applications?
The STM32L476QGI6 offers ultra-low power modes, consuming as little as 1 µA in Stop 2 mode. Its ARM Cortex-M4 core balances performance and energy efficiency, making it perfect for devices like IoT sensors and wearables.
Tip: Use its flexible power management to extend battery life in portable devices.
2. How does the STM32L476QGI6 compare to other STM32 microcontrollers?
This microcontroller outshines others with its advanced power-saving features and higher computational power. Its Stop 2 mode and dynamic voltage scaling provide unmatched energy efficiency, while its 19 ADC channels offer superior signal processing.
Note: It’s a great choice for energy-sensitive and performance-driven applications.
3. Can the STM32L476QGI6 handle harsh environments?
Yes, it operates reliably in temperatures from -40°C to 85°C. Its robust design and wide voltage range (1.71V to 3.6V) make it suitable for industrial and outdoor applications.
Example: Use it in energy-harvesting systems for remote monitoring.
4. What are the connectivity options available with the STM32L476QGI6?
The STM32L476QGI6 supports CANbus, I2C, SPI, UART, and USB OTG. These options ensure seamless communication between devices in various applications, from smart homes to industrial automation.
Tip: Leverage its connectivity for IoT networks or multi-device systems.
5. How does the STM32L476QGI6 support sustainability?
Its ultra-low power consumption reduces energy usage, lowering carbon emissions. By extending battery life, it minimizes electronic waste, making it an eco-friendly choice for modern designs.
Emoji: 🌱 Choose the STM32L476QGI6 for greener technology solutions.
Specifications
- TypeParameter
- Lifecycle Status
Lifecycle Status refers to the current stage of an electronic component in its product life cycle, indicating whether it is active, obsolete, or transitioning between these states. An active status means the component is in production and available for purchase. An obsolete status indicates that the component is no longer being manufactured or supported, and manufacturers typically provide a limited time frame for support. Understanding the lifecycle status is crucial for design engineers to ensure continuity and reliability in their projects.
ACTIVE (Last Updated: 7 months ago) - Factory Lead Time12 Weeks
- Mount
In electronic components, the term "Mount" typically refers to the method or process of physically attaching or fixing a component onto a circuit board or other electronic device. This can involve soldering, adhesive bonding, or other techniques to secure the component in place. The mounting process is crucial for ensuring proper electrical connections and mechanical stability within the electronic system. Different components may have specific mounting requirements based on their size, shape, and function, and manufacturers provide guidelines for proper mounting procedures to ensure optimal performance and reliability of the electronic device.
Surface Mount - Mounting Type
The "Mounting Type" in electronic components refers to the method used to attach or connect a component to a circuit board or other substrate, such as through-hole, surface-mount, or panel mount.
Surface Mount - Package / Case
refers to the protective housing that encases an electronic component, providing mechanical support, electrical connections, and thermal management.
132-UFBGA - Number of Pins132
- Data ConvertersA/D 19x12b; D/A 2x12b
- Number of I/Os109
- Operating Temperature
The operating temperature is the range of ambient temperature within which a power supply, or any other electrical equipment, operate in. This ranges from a minimum operating temperature, to a peak or maximum operating temperature, outside which, the power supply may fail.
-40°C~85°C TA - Packaging
Semiconductor package is a carrier / shell used to contain and cover one or more semiconductor components or integrated circuits. The material of the shell can be metal, plastic, glass or ceramic.
Tray - Series
In electronic components, the "Series" refers to a group of products that share similar characteristics, designs, or functionalities, often produced by the same manufacturer. These components within a series typically have common specifications but may vary in terms of voltage, power, or packaging to meet different application needs. The series name helps identify and differentiate between various product lines within a manufacturer's catalog.
STM32L4 - Part Status
Parts can have many statuses as they progress through the configuration, analysis, review, and approval stages.
Active - Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL)
Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) is a standardized rating that indicates the susceptibility of electronic components, particularly semiconductors, to moisture-induced damage during storage and the soldering process, defining the allowable exposure time to ambient conditions before they require special handling or baking to prevent failures
3 (168 Hours) - Number of Terminations132
- Terminal Position
In electronic components, the term "Terminal Position" refers to the physical location of the connection points on the component where external electrical connections can be made. These connection points, known as terminals, are typically used to attach wires, leads, or other components to the main body of the electronic component. The terminal position is important for ensuring proper connectivity and functionality of the component within a circuit. It is often specified in technical datasheets or component specifications to help designers and engineers understand how to properly integrate the component into their circuit designs.
BOTTOM - Terminal Form
Occurring at or forming the end of a series, succession, or the like; closing; concluding.
BALL - Supply Voltage
Supply voltage refers to the electrical potential difference provided to an electronic component or circuit. It is crucial for the proper operation of devices, as it powers their functions and determines performance characteristics. The supply voltage must be within specified limits to ensure reliability and prevent damage to components. Different electronic devices have specific supply voltage requirements, which can vary widely depending on their design and intended application.
3V - Terminal Pitch
The center distance from one pole to the next.
0.5mm - Frequency
In electronic components, the parameter "Frequency" refers to the rate at which a signal oscillates or cycles within a given period of time. It is typically measured in Hertz (Hz) and represents how many times a signal completes a full cycle in one second. Frequency is a crucial aspect in electronic components as it determines the behavior and performance of various devices such as oscillators, filters, and communication systems. Understanding the frequency characteristics of components is essential for designing and analyzing electronic circuits to ensure proper functionality and compatibility with other components in a system.
80MHz - Base Part Number
The "Base Part Number" (BPN) in electronic components serves a similar purpose to the "Base Product Number." It refers to the primary identifier for a component that captures the essential characteristics shared by a group of similar components. The BPN provides a fundamental way to reference a family or series of components without specifying all the variations and specific details.
STM32L476 - Supply Voltage-Max (Vsup)
The parameter "Supply Voltage-Max (Vsup)" in electronic components refers to the maximum voltage that can be safely applied to the component without causing damage. It is an important specification to consider when designing or using electronic circuits to ensure the component operates within its safe operating limits. Exceeding the maximum supply voltage can lead to overheating, component failure, or even permanent damage. It is crucial to adhere to the specified maximum supply voltage to ensure the reliable and safe operation of the electronic component.
3.6V - Supply Voltage-Min (Vsup)
The parameter "Supply Voltage-Min (Vsup)" in electronic components refers to the minimum voltage level required for the component to operate within its specified performance range. This parameter indicates the lowest voltage that can be safely applied to the component without risking damage or malfunction. It is crucial to ensure that the supply voltage provided to the component meets or exceeds this minimum value to ensure proper functionality and reliability. Failure to adhere to the specified minimum supply voltage may result in erratic behavior, reduced performance, or even permanent damage to the component.
1.71V - Memory Size
The memory capacity is the amount of data a device can store at any given time in its memory.
1MB - Oscillator Type
Wien Bridge Oscillator; RC Phase Shift Oscillator; Hartley Oscillator; Voltage Controlled Oscillator; Colpitts Oscillator; Clapp Oscillators; Crystal Oscillators; Armstrong Oscillator.
Internal - RAM Size
RAM size refers to the amount of random access memory (RAM) available in an electronic component, such as a computer or smartphone. RAM is a type of volatile memory that stores data and instructions that are actively being used by the device's processor. The RAM size is typically measured in gigabytes (GB) and determines how much data the device can store and access quickly for processing. A larger RAM size allows for smoother multitasking, faster loading times, and better overall performance of the electronic component. It is an important factor to consider when choosing a device, especially for tasks that require a lot of memory, such as gaming, video editing, or running multiple applications simultaneously.
128K x 8 - Voltage - Supply (Vcc/Vdd)
Voltage - Supply (Vcc/Vdd) is a key parameter in electronic components that specifies the voltage level required for the proper operation of the device. It represents the power supply voltage that needs to be provided to the component for it to function correctly. This parameter is crucial as supplying the component with the correct voltage ensures that it operates within its specified limits and performance characteristics. It is typically expressed in volts (V) and is an essential consideration when designing and using electronic circuits to prevent damage and ensure reliable operation.
1.71V~3.6V - uPs/uCs/Peripheral ICs Type
The parameter "uPs/uCs/Peripheral ICs Type" refers to the classification of various integrated circuits used in electronic devices. It encompasses microprocessors (uPs), microcontrollers (uCs), and peripheral integrated circuits that provide additional functionalities. This classification helps in identifying the specific type of chip used for processing tasks, controlling hardware, or interfacing with other components in a system. Understanding this parameter is essential for selecting the appropriate electronic components for a given application.
MICROCONTROLLER, RISC - Core Processor
The term "Core Processor" typically refers to the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer or electronic device. It is the primary component responsible for executing instructions, performing calculations, and managing data within the system. The core processor is often considered the brain of the device, as it controls the overall operation and functionality. It is crucial for determining the speed and performance capabilities of the device, as well as its ability to handle various tasks and applications efficiently. In modern devices, core processors can have multiple cores, allowing for parallel processing and improved multitasking capabilities.
ARM® Cortex®-M4 - Peripherals
In the context of electronic components, "Peripherals" refer to devices or components that are connected to a main system or device to enhance its functionality or provide additional features. These peripherals can include input devices such as keyboards, mice, and touchscreens, as well as output devices like monitors, printers, and speakers. Other examples of peripherals include external storage devices, network adapters, and cameras. Essentially, peripherals are external devices that expand the capabilities of a main electronic system or device.
Brown-out Detect/Reset, DMA, LCD, PWM, WDT - Program Memory Type
Program memory typically refers to flash memory when it is used to hold the program (instructions). Program memory may also refer to a hard drive or solid state drive (SSD). Contrast with data memory.
FLASH - Core Size
Core size in electronic components refers to the physical dimensions of the core material used in devices such as inductors and transformers. The core size directly impacts the performance characteristics of the component, including its inductance, saturation current, and frequency response. A larger core size typically allows for higher power handling capabilities and lower core losses, while a smaller core size may result in a more compact design but with limitations on power handling and efficiency. Designers must carefully select the core size based on the specific requirements of the application to achieve optimal performance and efficiency.
32-Bit - Program Memory Size
Program Memory Size refers to the amount of memory available in an electronic component, such as a microcontroller or microprocessor, that is used to store program instructions. This memory is non-volatile, meaning that the data stored in it is retained even when the power is turned off. The program memory size determines the maximum amount of code that can be stored and executed by the electronic component. It is an important parameter to consider when selecting a component for a specific application, as insufficient program memory size may limit the functionality or performance of the device.
1MB 1M x 8 - Connectivity
In electronic components, "Connectivity" refers to the ability of a component to establish and maintain connections with other components or devices within a circuit. It is a crucial parameter that determines how easily signals can be transmitted between different parts of a circuit. Connectivity can be influenced by factors such as the number of input and output ports, the type of connectors used, and the overall design of the component. Components with good connectivity are essential for ensuring reliable and efficient operation of electronic systems.
CANbus, EBI/EMI, I2C, IrDA, LINbus, MMC/SD, QSPI, SAI, SPI, SWPMI, UART/USART, USB OTG - Bit Size
In electronic components, "Bit Size" refers to the number of bits that can be processed or stored by a particular component. A bit is the smallest unit of data in computing and can have a value of either 0 or 1. The Bit Size parameter is commonly used to describe the capacity or performance of components such as microprocessors, memory modules, and data buses. A larger Bit Size generally indicates a higher processing capability or storage capacity, allowing for more complex operations and larger amounts of data to be handled efficiently. It is an important specification to consider when selecting electronic components for specific applications that require certain levels of performance and data processing capabilities.
32 - Has ADC
Has ADC refers to the presence of an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) in an electronic component. An ADC is a crucial component in many electronic devices as it converts analog signals, such as voltage or current, into digital data that can be processed by a digital system. Having an ADC allows the electronic component to interface with analog signals and convert them into a format that can be manipulated and analyzed digitally. This parameter is important for applications where analog signals need to be converted into digital form for further processing or control.
YES - DMA Channels
DMA (Direct Memory Access) Channels are a feature found in electronic components such as microcontrollers, microprocessors, and peripheral devices. DMA Channels allow data to be transferred directly between peripherals and memory without involving the CPU, thereby reducing the burden on the CPU and improving overall system performance. Each DMA Channel is typically assigned to a specific peripheral device or memory region, enabling efficient data transfer operations. The number of DMA Channels available in a system determines the concurrent data transfer capabilities and can vary depending on the specific hardware design. Overall, DMA Channels play a crucial role in optimizing data transfer efficiency and system performance in electronic devices.
YES - Data Rate
Data Rate is defined as the amount of data transmitted during a specified time period over a network. It is the speed at which data is transferred from one device to another or between a peripheral device and the computer. It is generally measured in Mega bits per second(Mbps) or Mega bytes per second(MBps).
5 Mbps - Data Bus Width
The data bus width in electronic components refers to the number of bits that can be transferred simultaneously between the processor and memory. It determines the amount of data that can be processed and transferred in a single operation. A wider data bus allows for faster data transfer speeds and improved overall performance of the electronic device. Common data bus widths include 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit, and 64-bit, with higher numbers indicating a larger capacity for data transfer. The data bus width is an important specification to consider when evaluating the speed and efficiency of a computer system or other electronic device.
32b - PWM Channels
PWM Channels, or Pulse Width Modulation Channels, refer to the number of independent PWM outputs available in an electronic component, such as a microcontroller or a motor driver. PWM is a technique used to generate analog-like signals by varying the duty cycle of a square wave signal. Each PWM channel can control the output of a specific device or component by adjusting the pulse width of the signal. Having multiple PWM channels allows for precise control of multiple devices simultaneously, making it a valuable feature in applications such as motor control, LED dimming, and audio signal generation. The number of PWM channels available in a component determines the flexibility and complexity of the system it can control.
YES - Number of Timers/Counters11
- Core Architecture
In electronic components, the term "Core Architecture" refers to the fundamental design and structure of the component's internal circuitry. It encompasses the arrangement of key components, such as processors, memory units, and input/output interfaces, within the device. The core architecture plays a crucial role in determining the component's performance, power efficiency, and overall capabilities. Different core architectures are optimized for specific applications and requirements, such as high-speed processing, low power consumption, or specialized functions. Understanding the core architecture of electronic components is essential for engineers and designers to select the most suitable components for their projects.
ARM - Number of ADC Channels19
- Height500μm
- Length7.05mm
- Width7.05mm
- REACH SVHC
The parameter "REACH SVHC" in electronic components refers to the compliance with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation regarding Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC). SVHCs are substances that may have serious effects on human health or the environment, and their use is regulated under REACH to ensure their safe handling and minimize their impact.Manufacturers of electronic components need to declare if their products contain any SVHCs above a certain threshold concentration and provide information on the safe use of these substances. This information allows customers to make informed decisions about the potential risks associated with using the components and take appropriate measures to mitigate any hazards.Ensuring compliance with REACH SVHC requirements is essential for electronics manufacturers to meet regulatory standards, protect human health and the environment, and maintain transparency in their supply chain. It also demonstrates a commitment to sustainability and responsible manufacturing practices in the electronics industry.
No SVHC - RoHS Status
RoHS means “Restriction of Certain Hazardous Substances” in the “Hazardous Substances Directive” in electrical and electronic equipment.
ROHS3 Compliant - Lead Free
Lead Free is a term used to describe electronic components that do not contain lead as part of their composition. Lead is a toxic material that can have harmful effects on human health and the environment, so the electronics industry has been moving towards lead-free components to reduce these risks. Lead-free components are typically made using alternative materials such as silver, copper, and tin. Manufacturers must comply with regulations such as the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive to ensure that their products are lead-free and environmentally friendly.
Lead Free
Parts with Similar Specs
- ImagePart NumberManufacturerPackage / CaseNumber of PinsCore ArchitectureData Bus WidthNumber of I/OMemory SizeSupply VoltagePeripheralsView Compare
STM32L476QGI6
132-UFBGA
132
ARM
32 b
109
1 MB
3 V
Brown-out Detect/Reset, DMA, LCD, PWM, WDT
132-UFBGA
132
ARM
32 b
109
1 MB
1.8 V
Brown-out Detect/Reset, DMA, LCD, PWM, WDT
144-LQFP
144
ARM
32 b
114
1 MB
1.8 V
Brown-out Detect/Reset, DMA, LCD, PWM, WDT
100-LQFP
100
ARM
32 b
82
1 MB
3 V
Brown-out Detect/Reset, DMA, LCD, PWM, WDT
100-LQFP
100
ARM
32 b
79
1 MB
1.2 V
Brown-out Detect/Reset, DMA, POR, PWM, WDT
Datasheet PDF
- Datasheets :
 Essential Tips for Resolving STM32F407ZET6 Connectivity Issues
Essential Tips for Resolving STM32F407ZET6 Connectivity Issues24 July 2025360
![A23 Energizer A23 Batteries Miniature Alkaline 12V [Video]: Datasheet, Application, and Equivalents](https://res.utmel.com/Images/Article/f7ee8460-e4da-4af6-933b-454755320e46.jpg) A23 Energizer A23 Batteries Miniature Alkaline 12V [Video]: Datasheet, Application, and Equivalents
A23 Energizer A23 Batteries Miniature Alkaline 12V [Video]: Datasheet, Application, and Equivalents25 March 20223014
 TPS22810DRVR Load Switch: Package, Pinout, and Datasheet
TPS22810DRVR Load Switch: Package, Pinout, and Datasheet29 March 20221341
 LT4320 Diode Bridge Controller: Pinout, Features and Datasheet
LT4320 Diode Bridge Controller: Pinout, Features and Datasheet06 November 20213791
 AD811 2500 V/µs High-Speed Op-Amp: Datasheet, Pinout, and Performance Analysis
AD811 2500 V/µs High-Speed Op-Amp: Datasheet, Pinout, and Performance Analysis04 March 202613
 TIP127 PNP Transistor: Pinout, Datasheet, and Test Circuit
TIP127 PNP Transistor: Pinout, Datasheet, and Test Circuit17 July 202111466
 A Comprehensive Guide to DIABLO16 Microcontroller by 4D Systems Pty Ltd
A Comprehensive Guide to DIABLO16 Microcontroller by 4D Systems Pty Ltd07 March 2024491
 RG6 VS RG59: Who is the winner?
RG6 VS RG59: Who is the winner?28 March 202224623
 What is Power over Ethernet(PoE)?
What is Power over Ethernet(PoE)?01 December 20212682
 What are Avalanche Diodes?
What are Avalanche Diodes?02 April 202012635
 An Overview of Linear Integrated Circuits
An Overview of Linear Integrated Circuits23 October 202511726
 Introduction to Servo System
Introduction to Servo System08 September 202114462
 What is Visible Light Communication(VLC)?
What is Visible Light Communication(VLC)?13 October 202114146
 Solid State Relay Basics: Working, Features and Structure
Solid State Relay Basics: Working, Features and Structure17 September 20209227
 Basis of Fiber Optic and Fiber Optic Communication
Basis of Fiber Optic and Fiber Optic Communication22 October 20214672
 Everything You Need to Know about NVMe
Everything You Need to Know about NVMe04 August 20215059
STMicroelectronics
In Stock: 10000
United States
China
Canada
Japan
Russia
Germany
United Kingdom
Singapore
Italy
Hong Kong(China)
Taiwan(China)
France
Korea
Mexico
Netherlands
Malaysia
Austria
Spain
Switzerland
Poland
Thailand
Vietnam
India
United Arab Emirates
Afghanistan
Åland Islands
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antigua & Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba
Bosnia & Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
Christmas Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo
Congo (DRC)
Cook Islands
Costa Rica
Côte d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curaçao
Cyprus
Czechia
Denmark
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia
Georgia
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Honduras
Hungary
Iceland
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Jamaica
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macao(China)
Madagascar
Malawi
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Myanmar
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Korea
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Palestinian Authority
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Réunion
Romania
Rwanda
Samoa
San Marino
São Tomé & Príncipe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
South Sudan
Sri Lanka
St Helena, Ascension, Tristan da Cunha
St. Barthélemy
St. Kitts & Nevis
St. Lucia
St. Martin
St. Pierre & Miquelon
St. Vincent & Grenadines
Sudan
Suriname
Svalbard & Jan Mayen
Sweden
Syria
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad & Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks & Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
U.S. Outlying Islands
U.S. Virgin Islands
Uganda
Ukraine
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Vatican City
Venezuela
Wallis & Futuna
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe


 Product
Product Brand
Brand Articles
Articles Tools
Tools







